README.md in rails_api_documentation-0.3.2 vs README.md in rails_api_documentation-0.3.3
- old
+ new
@@ -1,8 +1,7 @@
+# RailsApiDoc [](https://circleci.com/gh/vshaveyko/rails_api_doc/tree/master)
-# RailsApiDoc
-
## Installation
Add this line to your application's Gemfile:
```ruby
@@ -17,172 +16,179 @@
$ gem install rails_api_documentation
## Features
-+ displaying application api if used in one of correct ways
++ Displaying application api if used in one of the correct ways.
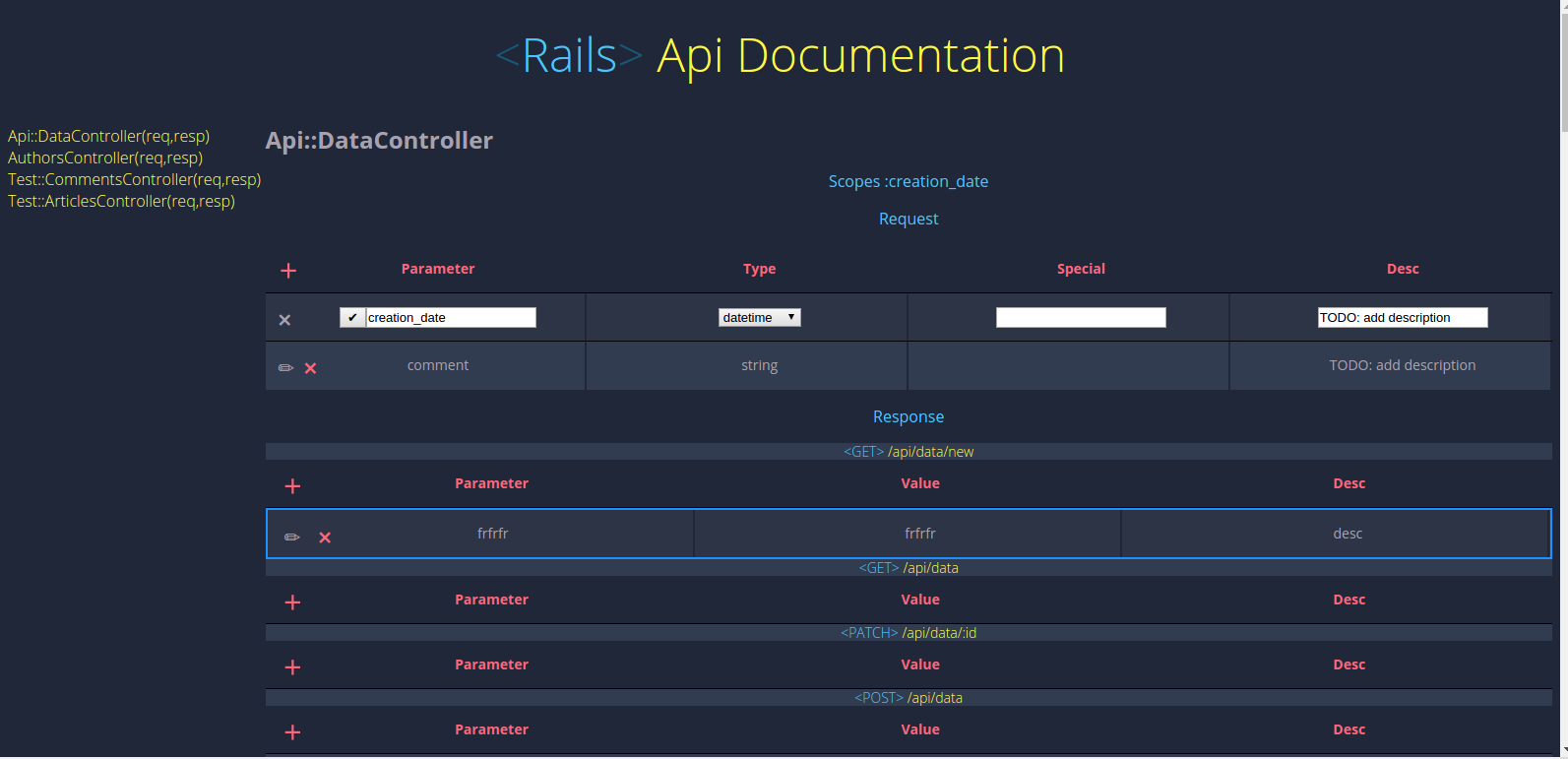
-+ Integration with Rabl if it is bundled
-+ ```strong_params``` method that will filter incoming params for you
++ Integration with Rabl if it is bundled.
++ `strong_params` method that will filter incoming params for you.
## Usage
To display api documentation on route '/api_doc' you need to:
-0. config/application.rb ->
+1. config/application.rb ->
```ruby
- require 'rails_api_doc'
+require 'rails_api_doc'
```
-1. config/routes.rb ->
- ```ruby
- mount RailsApiDoc::Engine => '/api_doc'
- ```
-2. define request parameters. Example:
- ```ruby
- class AuthorsController < ApplicationController
+2. config/routes.rb ->
+```ruby
+mount RailsApiDoc::Engine => '/api_doc'
+```
- has_scope :article_id, :name
+3. define request parameters. Example:
+```ruby
+class AuthorsController < ApplicationController
- # Define parameters with type and nested options
- # Article and Datum are usual ActiveRecord models
- parameter :age, type: :integer
- parameter :name, type: :string, required: true
- parameter :articles_attributes, type: :ary_object, model: 'Article' do
- parameter :title, type: :string
- parameter :body, type: :string, required: true
- parameter :rating, type: :enum, enum: [1, 2, 3]
- parameter :data_attributes, type: :object, model: 'Datum' do
- parameter :creation_date, type: :datetime
- parameter :comment, type: :string
- end
- end
- parameter :test, type: :string, required: true
+ has_scope :article_id, :name
- parameter({
- articles_attributes: { model: 'Article', type: :ary_object },
- data_attributes: { model: 'Datum' },
- comments_attributes: { model: 'Comment', type: :ary_object }
- }, type: :object) do
- parameter :id
- parameter :name
- end
-
+ # Define parameters with type and nested options
+ # Article and Datum are usual ActiveRecord models
+ parameter :age, type: :integer
+ parameter :name, type: :string, required: true
+ parameter :articles_attributes, type: :ary_object, model: 'Article' do
+ parameter :title, type: :string
+ parameter :body, type: :string, required: true
+ parameter :rating, type: :enum, enum: [1, 2, 3]
+ parameter :data_attributes, type: :object, model: 'Datum' do
+ parameter :creation_date, type: :datetime
+ parameter :comment, type: :string
end
- ```
-3. go to localhost:3000/api_doc
+ end
+ parameter :test, type: :string, required: true
-## Strong params
+ parameter({
+ articles_attributes: { model: 'Article', type: :ary_object },
+ data_attributes: { model: 'Datum' },
+ comments_attributes: { model: 'Comment', type: :ary_object }
+ }, type: :object) do
+ parameter :id
+ parameter :name
+ end
- You may want to use your defined request api to filter incoming parameters.
- Usually we use something like `params.permit(:name, :age)`, but no more!
- With this gem bundled you can do this:
+end
+```
- ```ruby
+4. go to localhost:3000/api_doc
- parameter :body, type: :string
- parameter :title, type: :string
+## Strong params
- # controller action
- def create
- Comment.create!(strong_params)
- end
+You may want to use your defined request api to filter incoming parameters.
+Usually we use something like `params.permit(:name, :age)`, but no more!
+With this gem bundled you can do this:
- ```
+```ruby
+parameter :body, type: :string
+parameter :title, type: :string
- and if request is `POST '/comments', params: { body: 'Comment body', title: 'Comment title', age: 34 }`
+# controller action
+def create
+ Comment.create!(strong_params)
+end
+```
- Comment will be created with: `Comment(body='Comment body', title='Comment title', age=nil)`
+and if request is `POST '/comments', params: { body: 'Comment body', title: 'Comment title', age: 34 }`
+Comment will be created with: `Comment(body='Comment body', title='Comment title', age=nil)`
+
## Value
- You can pass optional value argument to every parameter:
+You can pass optional value argument to every parameter:
- ```ruby
- parameter :val, type: :integer, value: -> (request_value) { 5 }
- ```
+```ruby
+parameter :val, type: :integer, value: -> (request_value) { 5 }
+```
- on every matching request value in this field will be overriden by value returned by proc.
+on every matching request value in this field will be overriden by value returned by proc.
- value field expecting anything that will respond to `:call` and can accept one argument(param value from request)
+value field expecting anything that will respond to `:call` and can accept one argument(param value from request)
- you should expect that value passed can be `nil`
+you should expect that value passed can be `nil`
- This can be used to force values on some fields, or modify values passed to request in some ways.
+This can be used to force values on some fields, or modify values passed to request in some ways.
- E.g. you want to force current_user_id on model creation instead of passing it from frontend.
+E.g. you want to force current_user_id on model creation instead of passing it from frontend.
## Enum
- When you defined parameter type as `:enum` you can pass `enum:` option. This will filter parameter by values provided.
+When you defined parameter type as `:enum` you can pass `enum:` option. This will filter parameter by values provided.
-## Group common blocks
+E.g.:
- You can define parameters that have common fields this way:
+```ruby
+parameter :rating, type: :enum, enum: [1, 2, 3]
+```
- ```ruby
- parameter({
- articles_attributes: { model: 'Article', type: :ary_object },
- data_attributes: { model: 'Datum' },
- comments_attributes: { model: 'Comment', type: :ary_object }
- }, type: :object) do
- parameter :id
- parameter :name
- end
- ```
+All enum values are parsed as strings, since controller params are always strings. Still you may write them as you want. Every member of enum array will be replaced with `&:to_s` version.
- Pass common values as last optional arguments and uniq definitions as hash value.
- All nesting parameters are applied to elements in blocks.
+## Group common blocks
- Something with same type can be defined like this:
+You can define parameters that have common fields this way:
- ```ruby
- parameter :name, :desc, type: :string
- ```
+```ruby
+parameter({
+ articles_attributes: { model: 'Article', type: :ary_object },
+ data_attributes: { model: 'Datum' },
+ comments_attributes: { model: 'Comment', type: :ary_object }
+}, type: :object) do
+ parameter :id
+ parameter :name
+end
+```
-## Types
+Pass common values as last optional arguments and uniq definitions as hash value.
+All nesting parameters are applied to elements in blocks.
- Parameter type may be one of these:
+Something with same type can be defined like this:
- ```ruby
+```ruby
+parameter :name, :desc, type: :string
+```
- # Non nested
- :bool - Boolean type, accepts true, false, 'true', 'false'
- :string - will accept anything beside nested type
- :integer - accepts numbers as string value, and usual numbers
- :array - array of atomic values (integer, strings, etc)
- :datetime - string with some datetime representation accepted by DateTime.parse
- :enum - one of predefined values of enum: option (only atomic types)
+## Types
- # nested
- :object - usual nested type. comes very handy with rails nested_attributes feature
- :ary_object - array of :object type, rails nested_attributes on has_many
+Parameter type may be one of these:
- ```
+```ruby
+# Non nested
+:bool - Boolean type, accepts true, false, 'true', 'false'
+:string - will accept anything beside nested type
+:integer - accepts numbers as string value, and usual numbers
+:array - array of atomic values (integer, strings, etc)
+:datetime - string with some datetime representation accepted by DateTime.parse
+:enum - one of predefined values of enum: option (only atomic types)
+:model - model reference e.g. :author_id, add model value as model: 'Author' after this
+# nested
+:object - usual nested type. comes very handy with rails nested_attributes feature
+:ary_object - array of :object type, rails nested_attributes on has_many
+```
+
## TODO's
+ type for id reference with model field to display associated model and CONTROLLER in params for linking
+ native DSL for defining response
```ruby
- action :show do
- response :age, type: Integer
- response :name, type String
- response :data, type: :model, model: Datum do
- response :creation_date, type: DateTime
- response :comment, type: String
- end
+action :show do
+ response :age, type: Integer
+ response :name, type String
+ response :data, type: :model, model: Datum do
+ response :creation_date, type: DateTime
+ response :comment, type: String
end
+end
```
+ native DSL for defining scopes
```ruby
scope :age, desc: 'Filters authors by given age'
```
+ dsl for extending response parameters
```ruby
- response :data, type: :model, model: Datum do
- extends DataController, action: :show
- end
+response :data, type: :model, model: Datum do
+ extends DataController, action: :show
+end
```
+ dsl for extending request parameters
```ruby
parameter :data, type: :model, model: Datum do
extends DataController, action: :show