Sidekiq Monitor
===============
Advanced monitoring for Sidekiq
Description
-----------
Sidekiq Monitor offers a detailed UI for monitoring Sidekiq jobs, letting you filter, search, and sort jobs by many attributes, view error backtraces, set job completion metadata, and more.
It lets you:
* Sort jobs by:
* Queue
* Class
* Queued at time
* Started at time
* Duration
* Status (e.g. queued, running, complete, failed)
* Filter jobs by:
* Queue
* Class
* Status
* Set and view metadata for each job:
* Name - A customizable, human-readable name (e.g. 'Data Import for John Doe')
* Result - A customizable value describing the job's result (e.g. '{imported\_documents\_count: 241, imported\_contacts_count: 183}')
* View errors for failed jobs, including a backtrace
* Easily isolate long-running jobs and failed jobs
* Retry failed jobs via a button-click
And it looks like this:
[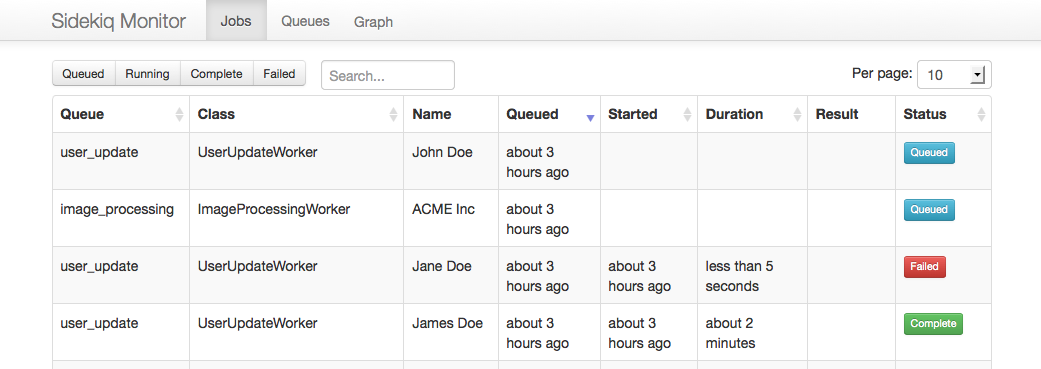 ](https://raw.github.com/socialpandas/sidekiq_monitor/master/examples/screenshot.png)
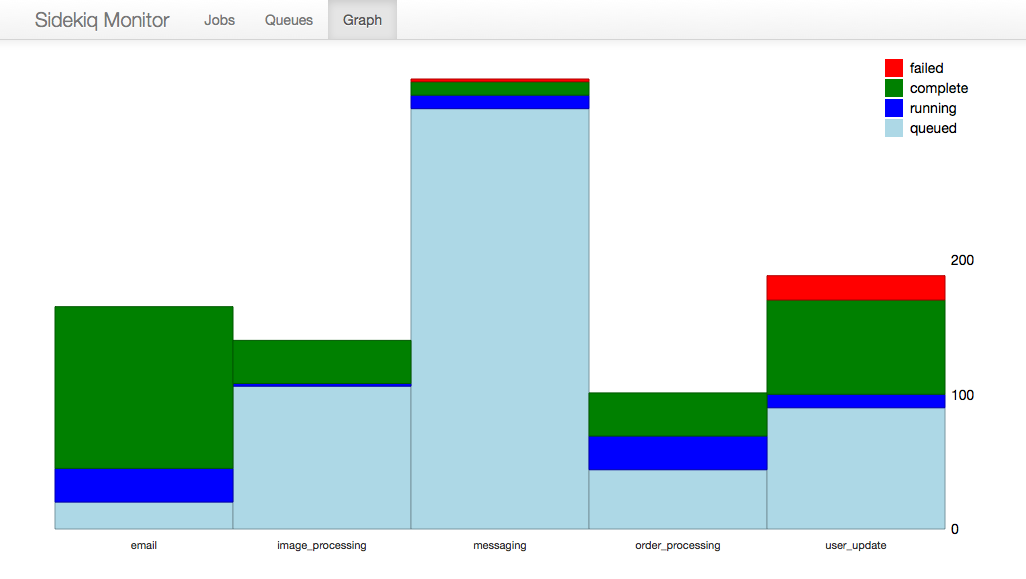
It also includes a live, stacked histogram showing the health of each queue:
[
](https://raw.github.com/socialpandas/sidekiq_monitor/master/examples/screenshot.png)
It also includes a live, stacked histogram showing the health of each queue:
[ ](https://raw.github.com/socialpandas/sidekiq_monitor/master/examples/screenshot.png)
Sidekiq Monitor stores jobs using ActiveRecord, allowing you to perform complex queries and delete specific collections of jobs:
```ruby
Sidekiq::Monitor::Job.where(queue: 'user_update').where('enqueued_at > ?', 2.days.ago).destroy_all
```
Installation
------------
Add sidekiq_monitor to your Gemfile:
gem 'sidekiq_monitor'
Install and run the migration:
rails g sidekiq:monitor:install
rake db:migrate
Mount it at a customizable path in `routes.rb`:
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
Usage
-----
### Setting a Job Name
To set a job's name (which makes the job's representation in the UI more human-readable), define a `self.job_name` method on your worker that takes the same arguments as its `perform` method:
```ruby
class HardWorker
include Sidekiq::Worker
def perform(user_id)
puts 'Doing hard work'
end
def self.job_name(user_id)
User.find(user_id).username
end
end
```
### Setting a Job Result
To set a job's result (which can show what the job accomplished, for example), return a hash from the worker's `perform` method:
```ruby
class HardWorker
include Sidekiq::Worker
def perform(user_ids)
puts 'Doing hard work'
{
message: "#{user_ids.length} users processed",
processed_users_count: user_ids.length
}
end
end
```
If you set `:message` as a key of this hash, that value will be displayed in the Result column of jobs tables in the UI. To view the full result hash of a job in the UI, click on the job status button to open up the modal job view.
### Graph
A single histogram will be shown by default in the Graph view, but you can also split the queues into multiple histograms. (This is especially useful if you have a large number of queues and the single histogram has too many bars to be readable.) The keys of this hash are JS regex patterns for matching queues, and the values of the hash will be the titles of each histogram:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:graphs] = {
'ALL' => 'All',
'OTHER' => 'Default Priority',
'_high$' => 'High Priority',
'_low$' => 'Low Priority'
}
```
`ALL` and `OTHER` are special keys: `ALL` will show all queues and `OTHER` will show all queues that aren't matched by the regex keys.
#### Poll Interval
The UI uses polling to update its data. By default, the polling interval is 3000ms, but you can adjust this like so:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:poll_interval] = 5000
```
### UI Customization
#### Custom Statuses
The UI's status filter and histograms show the most common job statuses, but if you'd like to add additional statuses to them (for example, if you want to show "interrupted" jobs or have added custom statuses through middleware), you can make the UI include them like so:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor::Job.add_status('interrupted')
```
#### Custom Job Views
When you click on a job, a modal showing its properties is displayed. You can add subviews to this modal by creating a view in your app and calling `Sidekiq::Monitor::CustomViews.add`, passing it the subview's title, the subview's filepath, and a block. The subview is only rendered if the block evaluates to true for the given job.
If you need to add JavaScript for the subview, you can do so by adding an asset path to `Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:javascripts]`.
For example, the following code adds a subview that shows a "Retry" button for jobs with the specified statuses:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
view_path = Rails.root.join('app', 'views', 'sidekiq', 'monitor', 'retry').to_s
Sidekiq::Monitor::CustomViews.add('My View Title', view_path) do |job|
%w{complete failed}.include?(job.status)
end
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:javascripts] << 'sidekiq/monitor/retry'
```
```
/ app/views/sidekiq/monitor/retry.slim
a class='btn btn-success' href='#' data-action='retry_job' data-job-id=job.id = 'Retry'
```
```coffee
# app/assets/javascripts/sidekiq/monitor/retry.js.coffee
$ ->
$('body').on 'click', '.job-modal [data-action=retry_job]', (e) ->
id = $(e.target).attr('data-job-id')
$.get SidekiqMonitor.settings.api_url("jobs/retry/#{id}")
alert 'Job has been retried'
false
```
### Authentication
You'll likely want to restrict access to this interface in a production setting. To do this, you can use routing constraints:
#### Devise
Checks a `User` model instance that responds to `admin?`
```ruby
constraint = lambda { |request| request.env["warden"].authenticate? and request.env['warden'].user.admin? }
constraints constraint do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
Allow any authenticated `User`
```ruby
constraint = lambda { |request| request.env['warden'].authenticate!({ scope: :user }) }
constraints constraint do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
Short version
```ruby
authenticate :user do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
#### Authlogic
```ruby
# lib/admin_constraint.rb
class AdminConstraint
def matches?(request)
return false unless request.cookies['user_credentials'].present?
user = User.find_by_persistence_token(request.cookies['user_credentials'].split(':')[0])
user && user.admin?
end
end
# config/routes.rb
require "admin_constraint"
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq', :constraints => AdminConstraint.new
```
#### Restful Authentication
Checks a `User` model instance that responds to `admin?`
```
# lib/admin_constraint.rb
class AdminConstraint
def matches?(request)
return false unless request.session[:user_id]
user = User.find request.session[:user_id]
user && user.admin?
end
end
# config/routes.rb
require "admin_constraint"
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq', :constraints => AdminConstraint.new
```
#### Custom External Authentication
```ruby
class AuthConstraint
def self.admin?(request)
return false unless (cookie = request.cookies['auth'])
Rails.cache.fetch(cookie['user'], :expires_in => 1.minute) do
auth_data = JSON.parse(Base64.decode64(cookie['data']))
response = HTTParty.post(Auth.validate_url, :query => auth_data)
response.code == 200 && JSON.parse(response.body)['roles'].to_a.include?('Admin')
end
end
end
# config/routes.rb
constraints lambda {|request| AuthConstraint.admin?(request) } do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/admin/sidekiq'
end
```
_(This authentication documentation was borrowed from the [Sidekiq wiki](https://github.com/mperham/sidekiq/wiki/Monitoring).)_
License
-------
Sidekiq Monitor is released under the MIT License. Please see the MIT-LICENSE file for details.
](https://raw.github.com/socialpandas/sidekiq_monitor/master/examples/screenshot.png)
Sidekiq Monitor stores jobs using ActiveRecord, allowing you to perform complex queries and delete specific collections of jobs:
```ruby
Sidekiq::Monitor::Job.where(queue: 'user_update').where('enqueued_at > ?', 2.days.ago).destroy_all
```
Installation
------------
Add sidekiq_monitor to your Gemfile:
gem 'sidekiq_monitor'
Install and run the migration:
rails g sidekiq:monitor:install
rake db:migrate
Mount it at a customizable path in `routes.rb`:
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
Usage
-----
### Setting a Job Name
To set a job's name (which makes the job's representation in the UI more human-readable), define a `self.job_name` method on your worker that takes the same arguments as its `perform` method:
```ruby
class HardWorker
include Sidekiq::Worker
def perform(user_id)
puts 'Doing hard work'
end
def self.job_name(user_id)
User.find(user_id).username
end
end
```
### Setting a Job Result
To set a job's result (which can show what the job accomplished, for example), return a hash from the worker's `perform` method:
```ruby
class HardWorker
include Sidekiq::Worker
def perform(user_ids)
puts 'Doing hard work'
{
message: "#{user_ids.length} users processed",
processed_users_count: user_ids.length
}
end
end
```
If you set `:message` as a key of this hash, that value will be displayed in the Result column of jobs tables in the UI. To view the full result hash of a job in the UI, click on the job status button to open up the modal job view.
### Graph
A single histogram will be shown by default in the Graph view, but you can also split the queues into multiple histograms. (This is especially useful if you have a large number of queues and the single histogram has too many bars to be readable.) The keys of this hash are JS regex patterns for matching queues, and the values of the hash will be the titles of each histogram:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:graphs] = {
'ALL' => 'All',
'OTHER' => 'Default Priority',
'_high$' => 'High Priority',
'_low$' => 'Low Priority'
}
```
`ALL` and `OTHER` are special keys: `ALL` will show all queues and `OTHER` will show all queues that aren't matched by the regex keys.
#### Poll Interval
The UI uses polling to update its data. By default, the polling interval is 3000ms, but you can adjust this like so:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:poll_interval] = 5000
```
### UI Customization
#### Custom Statuses
The UI's status filter and histograms show the most common job statuses, but if you'd like to add additional statuses to them (for example, if you want to show "interrupted" jobs or have added custom statuses through middleware), you can make the UI include them like so:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor::Job.add_status('interrupted')
```
#### Custom Job Views
When you click on a job, a modal showing its properties is displayed. You can add subviews to this modal by creating a view in your app and calling `Sidekiq::Monitor::CustomViews.add`, passing it the subview's title, the subview's filepath, and a block. The subview is only rendered if the block evaluates to true for the given job.
If you need to add JavaScript for the subview, you can do so by adding an asset path to `Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:javascripts]`.
For example, the following code adds a subview that shows a "Retry" button for jobs with the specified statuses:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
view_path = Rails.root.join('app', 'views', 'sidekiq', 'monitor', 'retry').to_s
Sidekiq::Monitor::CustomViews.add('My View Title', view_path) do |job|
%w{complete failed}.include?(job.status)
end
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:javascripts] << 'sidekiq/monitor/retry'
```
```
/ app/views/sidekiq/monitor/retry.slim
a class='btn btn-success' href='#' data-action='retry_job' data-job-id=job.id = 'Retry'
```
```coffee
# app/assets/javascripts/sidekiq/monitor/retry.js.coffee
$ ->
$('body').on 'click', '.job-modal [data-action=retry_job]', (e) ->
id = $(e.target).attr('data-job-id')
$.get SidekiqMonitor.settings.api_url("jobs/retry/#{id}")
alert 'Job has been retried'
false
```
### Authentication
You'll likely want to restrict access to this interface in a production setting. To do this, you can use routing constraints:
#### Devise
Checks a `User` model instance that responds to `admin?`
```ruby
constraint = lambda { |request| request.env["warden"].authenticate? and request.env['warden'].user.admin? }
constraints constraint do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
Allow any authenticated `User`
```ruby
constraint = lambda { |request| request.env['warden'].authenticate!({ scope: :user }) }
constraints constraint do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
Short version
```ruby
authenticate :user do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
#### Authlogic
```ruby
# lib/admin_constraint.rb
class AdminConstraint
def matches?(request)
return false unless request.cookies['user_credentials'].present?
user = User.find_by_persistence_token(request.cookies['user_credentials'].split(':')[0])
user && user.admin?
end
end
# config/routes.rb
require "admin_constraint"
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq', :constraints => AdminConstraint.new
```
#### Restful Authentication
Checks a `User` model instance that responds to `admin?`
```
# lib/admin_constraint.rb
class AdminConstraint
def matches?(request)
return false unless request.session[:user_id]
user = User.find request.session[:user_id]
user && user.admin?
end
end
# config/routes.rb
require "admin_constraint"
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq', :constraints => AdminConstraint.new
```
#### Custom External Authentication
```ruby
class AuthConstraint
def self.admin?(request)
return false unless (cookie = request.cookies['auth'])
Rails.cache.fetch(cookie['user'], :expires_in => 1.minute) do
auth_data = JSON.parse(Base64.decode64(cookie['data']))
response = HTTParty.post(Auth.validate_url, :query => auth_data)
response.code == 200 && JSON.parse(response.body)['roles'].to_a.include?('Admin')
end
end
end
# config/routes.rb
constraints lambda {|request| AuthConstraint.admin?(request) } do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/admin/sidekiq'
end
```
_(This authentication documentation was borrowed from the [Sidekiq wiki](https://github.com/mperham/sidekiq/wiki/Monitoring).)_
License
-------
Sidekiq Monitor is released under the MIT License. Please see the MIT-LICENSE file for details. ](https://raw.github.com/socialpandas/sidekiq_monitor/master/examples/screenshot.png)
It also includes a live, stacked histogram showing the health of each queue:
[
](https://raw.github.com/socialpandas/sidekiq_monitor/master/examples/screenshot.png)
It also includes a live, stacked histogram showing the health of each queue:
[ ](https://raw.github.com/socialpandas/sidekiq_monitor/master/examples/screenshot.png)
Sidekiq Monitor stores jobs using ActiveRecord, allowing you to perform complex queries and delete specific collections of jobs:
```ruby
Sidekiq::Monitor::Job.where(queue: 'user_update').where('enqueued_at > ?', 2.days.ago).destroy_all
```
Installation
------------
Add sidekiq_monitor to your Gemfile:
gem 'sidekiq_monitor'
Install and run the migration:
rails g sidekiq:monitor:install
rake db:migrate
Mount it at a customizable path in `routes.rb`:
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
Usage
-----
### Setting a Job Name
To set a job's name (which makes the job's representation in the UI more human-readable), define a `self.job_name` method on your worker that takes the same arguments as its `perform` method:
```ruby
class HardWorker
include Sidekiq::Worker
def perform(user_id)
puts 'Doing hard work'
end
def self.job_name(user_id)
User.find(user_id).username
end
end
```
### Setting a Job Result
To set a job's result (which can show what the job accomplished, for example), return a hash from the worker's `perform` method:
```ruby
class HardWorker
include Sidekiq::Worker
def perform(user_ids)
puts 'Doing hard work'
{
message: "#{user_ids.length} users processed",
processed_users_count: user_ids.length
}
end
end
```
If you set `:message` as a key of this hash, that value will be displayed in the Result column of jobs tables in the UI. To view the full result hash of a job in the UI, click on the job status button to open up the modal job view.
### Graph
A single histogram will be shown by default in the Graph view, but you can also split the queues into multiple histograms. (This is especially useful if you have a large number of queues and the single histogram has too many bars to be readable.) The keys of this hash are JS regex patterns for matching queues, and the values of the hash will be the titles of each histogram:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:graphs] = {
'ALL' => 'All',
'OTHER' => 'Default Priority',
'_high$' => 'High Priority',
'_low$' => 'Low Priority'
}
```
`ALL` and `OTHER` are special keys: `ALL` will show all queues and `OTHER` will show all queues that aren't matched by the regex keys.
#### Poll Interval
The UI uses polling to update its data. By default, the polling interval is 3000ms, but you can adjust this like so:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:poll_interval] = 5000
```
### UI Customization
#### Custom Statuses
The UI's status filter and histograms show the most common job statuses, but if you'd like to add additional statuses to them (for example, if you want to show "interrupted" jobs or have added custom statuses through middleware), you can make the UI include them like so:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor::Job.add_status('interrupted')
```
#### Custom Job Views
When you click on a job, a modal showing its properties is displayed. You can add subviews to this modal by creating a view in your app and calling `Sidekiq::Monitor::CustomViews.add`, passing it the subview's title, the subview's filepath, and a block. The subview is only rendered if the block evaluates to true for the given job.
If you need to add JavaScript for the subview, you can do so by adding an asset path to `Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:javascripts]`.
For example, the following code adds a subview that shows a "Retry" button for jobs with the specified statuses:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
view_path = Rails.root.join('app', 'views', 'sidekiq', 'monitor', 'retry').to_s
Sidekiq::Monitor::CustomViews.add('My View Title', view_path) do |job|
%w{complete failed}.include?(job.status)
end
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:javascripts] << 'sidekiq/monitor/retry'
```
```
/ app/views/sidekiq/monitor/retry.slim
a class='btn btn-success' href='#' data-action='retry_job' data-job-id=job.id = 'Retry'
```
```coffee
# app/assets/javascripts/sidekiq/monitor/retry.js.coffee
$ ->
$('body').on 'click', '.job-modal [data-action=retry_job]', (e) ->
id = $(e.target).attr('data-job-id')
$.get SidekiqMonitor.settings.api_url("jobs/retry/#{id}")
alert 'Job has been retried'
false
```
### Authentication
You'll likely want to restrict access to this interface in a production setting. To do this, you can use routing constraints:
#### Devise
Checks a `User` model instance that responds to `admin?`
```ruby
constraint = lambda { |request| request.env["warden"].authenticate? and request.env['warden'].user.admin? }
constraints constraint do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
Allow any authenticated `User`
```ruby
constraint = lambda { |request| request.env['warden'].authenticate!({ scope: :user }) }
constraints constraint do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
Short version
```ruby
authenticate :user do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
#### Authlogic
```ruby
# lib/admin_constraint.rb
class AdminConstraint
def matches?(request)
return false unless request.cookies['user_credentials'].present?
user = User.find_by_persistence_token(request.cookies['user_credentials'].split(':')[0])
user && user.admin?
end
end
# config/routes.rb
require "admin_constraint"
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq', :constraints => AdminConstraint.new
```
#### Restful Authentication
Checks a `User` model instance that responds to `admin?`
```
# lib/admin_constraint.rb
class AdminConstraint
def matches?(request)
return false unless request.session[:user_id]
user = User.find request.session[:user_id]
user && user.admin?
end
end
# config/routes.rb
require "admin_constraint"
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq', :constraints => AdminConstraint.new
```
#### Custom External Authentication
```ruby
class AuthConstraint
def self.admin?(request)
return false unless (cookie = request.cookies['auth'])
Rails.cache.fetch(cookie['user'], :expires_in => 1.minute) do
auth_data = JSON.parse(Base64.decode64(cookie['data']))
response = HTTParty.post(Auth.validate_url, :query => auth_data)
response.code == 200 && JSON.parse(response.body)['roles'].to_a.include?('Admin')
end
end
end
# config/routes.rb
constraints lambda {|request| AuthConstraint.admin?(request) } do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/admin/sidekiq'
end
```
_(This authentication documentation was borrowed from the [Sidekiq wiki](https://github.com/mperham/sidekiq/wiki/Monitoring).)_
License
-------
Sidekiq Monitor is released under the MIT License. Please see the MIT-LICENSE file for details.
](https://raw.github.com/socialpandas/sidekiq_monitor/master/examples/screenshot.png)
Sidekiq Monitor stores jobs using ActiveRecord, allowing you to perform complex queries and delete specific collections of jobs:
```ruby
Sidekiq::Monitor::Job.where(queue: 'user_update').where('enqueued_at > ?', 2.days.ago).destroy_all
```
Installation
------------
Add sidekiq_monitor to your Gemfile:
gem 'sidekiq_monitor'
Install and run the migration:
rails g sidekiq:monitor:install
rake db:migrate
Mount it at a customizable path in `routes.rb`:
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
Usage
-----
### Setting a Job Name
To set a job's name (which makes the job's representation in the UI more human-readable), define a `self.job_name` method on your worker that takes the same arguments as its `perform` method:
```ruby
class HardWorker
include Sidekiq::Worker
def perform(user_id)
puts 'Doing hard work'
end
def self.job_name(user_id)
User.find(user_id).username
end
end
```
### Setting a Job Result
To set a job's result (which can show what the job accomplished, for example), return a hash from the worker's `perform` method:
```ruby
class HardWorker
include Sidekiq::Worker
def perform(user_ids)
puts 'Doing hard work'
{
message: "#{user_ids.length} users processed",
processed_users_count: user_ids.length
}
end
end
```
If you set `:message` as a key of this hash, that value will be displayed in the Result column of jobs tables in the UI. To view the full result hash of a job in the UI, click on the job status button to open up the modal job view.
### Graph
A single histogram will be shown by default in the Graph view, but you can also split the queues into multiple histograms. (This is especially useful if you have a large number of queues and the single histogram has too many bars to be readable.) The keys of this hash are JS regex patterns for matching queues, and the values of the hash will be the titles of each histogram:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:graphs] = {
'ALL' => 'All',
'OTHER' => 'Default Priority',
'_high$' => 'High Priority',
'_low$' => 'Low Priority'
}
```
`ALL` and `OTHER` are special keys: `ALL` will show all queues and `OTHER` will show all queues that aren't matched by the regex keys.
#### Poll Interval
The UI uses polling to update its data. By default, the polling interval is 3000ms, but you can adjust this like so:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:poll_interval] = 5000
```
### UI Customization
#### Custom Statuses
The UI's status filter and histograms show the most common job statuses, but if you'd like to add additional statuses to them (for example, if you want to show "interrupted" jobs or have added custom statuses through middleware), you can make the UI include them like so:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
Sidekiq::Monitor::Job.add_status('interrupted')
```
#### Custom Job Views
When you click on a job, a modal showing its properties is displayed. You can add subviews to this modal by creating a view in your app and calling `Sidekiq::Monitor::CustomViews.add`, passing it the subview's title, the subview's filepath, and a block. The subview is only rendered if the block evaluates to true for the given job.
If you need to add JavaScript for the subview, you can do so by adding an asset path to `Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:javascripts]`.
For example, the following code adds a subview that shows a "Retry" button for jobs with the specified statuses:
```ruby
# config/initializers/sidekiq_monitor.rb
view_path = Rails.root.join('app', 'views', 'sidekiq', 'monitor', 'retry').to_s
Sidekiq::Monitor::CustomViews.add('My View Title', view_path) do |job|
%w{complete failed}.include?(job.status)
end
Sidekiq::Monitor.options[:javascripts] << 'sidekiq/monitor/retry'
```
```
/ app/views/sidekiq/monitor/retry.slim
a class='btn btn-success' href='#' data-action='retry_job' data-job-id=job.id = 'Retry'
```
```coffee
# app/assets/javascripts/sidekiq/monitor/retry.js.coffee
$ ->
$('body').on 'click', '.job-modal [data-action=retry_job]', (e) ->
id = $(e.target).attr('data-job-id')
$.get SidekiqMonitor.settings.api_url("jobs/retry/#{id}")
alert 'Job has been retried'
false
```
### Authentication
You'll likely want to restrict access to this interface in a production setting. To do this, you can use routing constraints:
#### Devise
Checks a `User` model instance that responds to `admin?`
```ruby
constraint = lambda { |request| request.env["warden"].authenticate? and request.env['warden'].user.admin? }
constraints constraint do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
Allow any authenticated `User`
```ruby
constraint = lambda { |request| request.env['warden'].authenticate!({ scope: :user }) }
constraints constraint do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
Short version
```ruby
authenticate :user do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq'
end
```
#### Authlogic
```ruby
# lib/admin_constraint.rb
class AdminConstraint
def matches?(request)
return false unless request.cookies['user_credentials'].present?
user = User.find_by_persistence_token(request.cookies['user_credentials'].split(':')[0])
user && user.admin?
end
end
# config/routes.rb
require "admin_constraint"
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq', :constraints => AdminConstraint.new
```
#### Restful Authentication
Checks a `User` model instance that responds to `admin?`
```
# lib/admin_constraint.rb
class AdminConstraint
def matches?(request)
return false unless request.session[:user_id]
user = User.find request.session[:user_id]
user && user.admin?
end
end
# config/routes.rb
require "admin_constraint"
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/sidekiq', :constraints => AdminConstraint.new
```
#### Custom External Authentication
```ruby
class AuthConstraint
def self.admin?(request)
return false unless (cookie = request.cookies['auth'])
Rails.cache.fetch(cookie['user'], :expires_in => 1.minute) do
auth_data = JSON.parse(Base64.decode64(cookie['data']))
response = HTTParty.post(Auth.validate_url, :query => auth_data)
response.code == 200 && JSON.parse(response.body)['roles'].to_a.include?('Admin')
end
end
end
# config/routes.rb
constraints lambda {|request| AuthConstraint.admin?(request) } do
mount Sidekiq::Monitor::Engine => '/admin/sidekiq'
end
```
_(This authentication documentation was borrowed from the [Sidekiq wiki](https://github.com/mperham/sidekiq/wiki/Monitoring).)_
License
-------
Sidekiq Monitor is released under the MIT License. Please see the MIT-LICENSE file for details.