# Puppet Check
[](https://travis-ci.org/mschuchard/puppet-check)
- [Description](#description)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [CLI](#cli)
- [Rake](#rake)
- [Exit Codes](#exit-codes)
- [Optional Dependencies](#optional-dependencies)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
## Description
Puppet Check is a gem that provides a comprehensive, streamlined, and efficient analysis of the syntax, style, and validity of your entire Puppet code and data.
### Former Method for Code and Data Checks
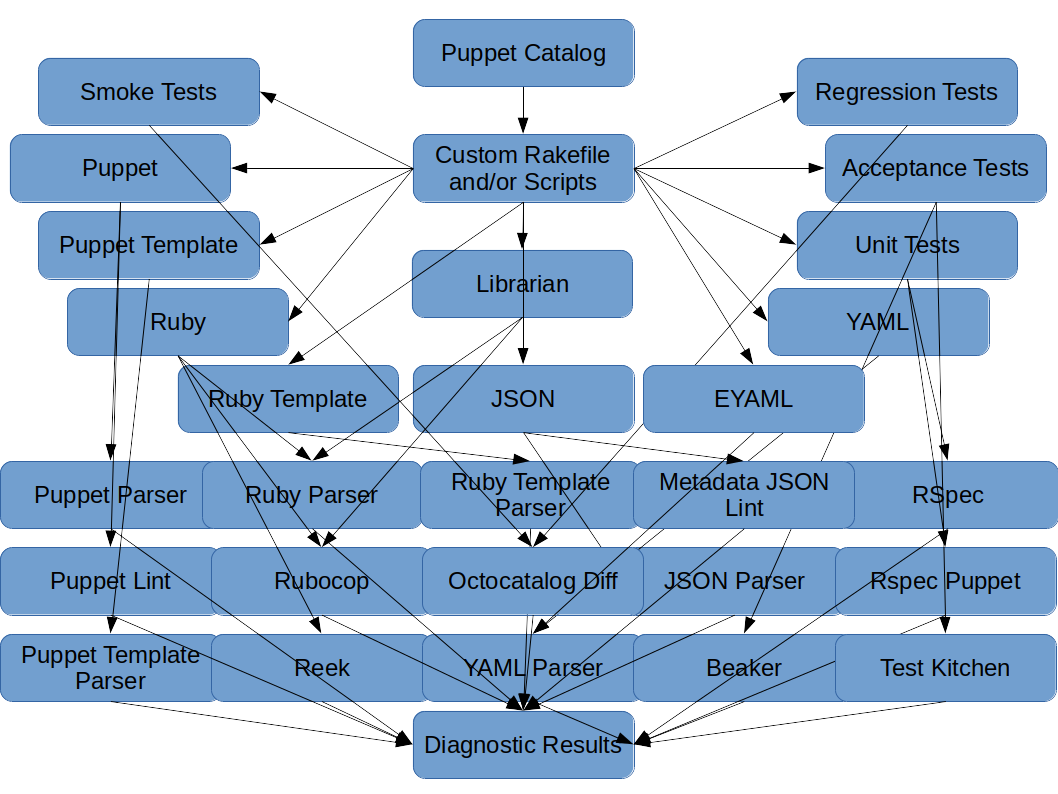
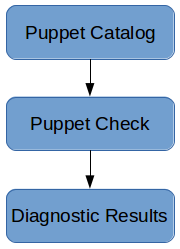
### Puppet Check Method for Code and Data Checks
### Example Output
```
The following files have errors:
-- manifests/syntax.pp:
This Variable has no effect. A value was produced and then forgotten (one or more preceding expressions may have the wrong form) at 1:1
Illegal variable name, The given name '' does not conform to the naming rule /^((::)?[a-z]\w*)*((::)?[a-z_]\w*)$/ at 1:1
Found 2 errors. Giving up
-- templates/syntax.epp:
This Name has no effect. A value was produced and then forgotten (one or more preceding expressions may have the wrong form) at 2:4
-- lib/syntax.rb:
(eval):1: syntax error, unexpected =>, expecting end-of-input
BEGIN {throw :good}; i => am : a '' ruby.file { with } &bad syntax
^
-- templates/syntax.erb:
(erb):1: syntax error, unexpected tIDENTIFIER, expecting ')'
... am "; _erbout.concat(( @a ruby ).to_s); _erbout.concat " te...
... ^
-- hieradata/syntax.yaml:
block sequence entries are not allowed in this context at line 2 column 4
-- hieradata/syntax.json:
757: unexpected token at '{
-- metadata_syntax/metadata.json:
Required field 'version' not found in metadata.json.
Duplicate dependencies on puppetlabs/nothing.
Deprecated field 'checksum' found.
Summary exceeds 144 characters.
-- librarian_syntax/Puppetfile:
(eval):3: syntax error, unexpected ':', expecting end-of-input
librarian: 'puppet'
^
The following files have warnings:
-- manifests/style_lint.pp:
double quoted string containing no variables at line 2, column 8
indentation of => is not properly aligned at line 2, column 5
-- manifests/style_parser.pp:
Unrecognized escape sequence '\[' at 2:77
Unrecognized escape sequence '\]' at 2:77
double quoted string containing no variables at line 2, column 45
-- lib/style.rb:
1:1: W: Useless assignment to variable - `hash`.
1:10: C: Use the new Ruby 1.9 hash syntax.
2:1: C: Do not introduce global variables.
3:6: C: Prefer single-quoted strings when you don't need string interpolation or special symbols.
[7]:Attribute: Issue#foobarbaz is a writable attribute [https://github.com/troessner/reek/blob/master/docs/Attribute.md]
[6]:IrresponsibleModule: Issue has no descriptive comment [https://github.com/troessner/reek/blob/master/docs/Irresponsible-Module.md]
-- templates/style.erb:
3: already initialized constant TEMPLATE
2: previous definition of TEMPLATE was here
-- hieradata/style.yaml:
Value(s) missing in key 'value'.
Value(s) missing in key 'and'.
-- metadata_style/metadata.json:
License identifier 'Imaginary' is not in the SPDX list: http://spdx.org/licenses/
-- librarian_style/Puppetfile:
2:3: C: Align the parameters of a method call if they span more than one line.
5:13: C: Use the new Ruby 1.9 hash syntax.
The following files have no errors or warnings:
-- manifests/good.pp
-- templates/good.epp
-- lib/good.rb
-- templates/good.erb
-- hieradata/good.yaml
-- hieradata/good.json
-- metadata_good/metadata.json
-- librarian_good/Puppetfile
The following files have unrecognized formats and therefore were not processed:
-- foobarbaz
```
### Why not Puppetlabs Spec Helper?
- Puppetlabs Spec Helper is focused more on advanced and robust spec testing. Puppet Check is focused more on efficient and comprehensive Puppet code and data validation.
- Puppetlabs Spec Helper performs fewer types of checks.
- Puppetlabs Spec Helper has extra layers of gems in between it and the gems executing the checks.
- Puppetlabs Spec Helper does not allow interfacing through it to the gems executing the checks.
- Puppetlabs Spec Helper has no CLI.
- Puppetlabs Spec Helper intrinsically only executes spec tests against one module at a time.
- Puppetlabs Spec Helper requires an additional config file for RSpec Puppet support.
It is worth nothing that there is no current development objective for Puppet Check to achieve the same advanced level of robustness for spec testing that Puppetlabs Spec Helper enables. If you are performing standard spec testing on your Puppet code and data, then Puppet Check's spec testing is a fantastic lightweight and faster alternative to Puppetlabs Spec Helper. If you require advanced and intricate capabilities in your spec testing (e.g. direct interfacing to the `Puppet::Parser::Scope` API), you will likely prefer Puppetlabs Spec Helper's spec testing in conjunction with Puppet Check's file validation.
## Usage
Puppet Check requires `ruby >= 1.9.3`, `puppet >= 3.2`, and `puppet-lint >= 1.1.0`. All other dependencies should be fine with various versions. Puppet Check can be used either with a CLI or Rake tasks. Please note both interfaces will ignore any directories named `fixtures` or specified paths with that directory during file checks.
### CLI
```
usage: puppet-check [options] paths
-f, --future Enable future parser
-s, --style Enable style checks
--puppet-lint arg_one,arg_two
Arguments for PuppetLint ignored checks
-c, --config file Load PuppetLint options from file.
--rubocop arg_one,arg_two Arguments for Rubocop disabled cops
```
The command line interface enables the ability to select the Puppet future parser, additional style checks besides the syntax checks, and to specify PuppetLint and Rubocop checks to ignore. If you require a more robust interface to PuppetLint, Rubocop, and Reek, then please use `.puppet-lint.rc`, `.rubocop.yml` and `*.reek` config files. The `.puppet-lint.rc` can be specified with the `-c` argument. If it is not specified, then PuppetLint will automatically load one from `.puppet-lint.rc`, `~/.puppet-lint.rc`, or `/etc/puppet-lint.rc`, in that order of preference. The nearest `.rubocop.yml` and `*.reek` will be automatically respected.
Example:
```
puppet-check -s --puppet-lint no-hard_tabs-check,no-80chars-check --rubocop Metrics/LineLength,Style/Encoding path/to/code_and_data
```
### Rake
Interfacing with Puppet-Check via `rake` requires a `require puppet-check/tasks` in your Rakefile. This generates the following `rake` commands:
```
rake puppetcheck # Execute all Puppet-Check checks
rake puppetcheck:file # Execute Puppet-Check file checks
rake puppetcheck:spec # Execute RSpec and RSpec-Puppet tests
rake puppetcheck:beaker # Execute Beaker acceptance tests
```
#### puppetcheck:file
You can add style checks to and select the future parser for the `rake puppetcheck:file` by adding the following after the require:
```ruby
PuppetCheck.style_check = true
PuppetCheck.future_parser = true
```
The style checks from within `rake puppetcheck:file` are directly interfaced to `puppet-lint`, `rubocop`, and `reek`. This means that all arguments and options should be specified from within your `.puppet-lint.rc`, `.rubocop.yml`, and `*.reek`. The capability to pass style arguments and options from within the `Rakefile` task block will be considered for future versions.
#### puppetcheck:spec
The spec tests will be executed against everything that matches the pattern `**/{classes, defines, facter, functions, hosts, puppet, unit, types}/**/*_spec.rb`. This means everything in the current path that appears to be a Puppet module spec test will be regarded as such and executed during this rake task.
Please note it is perfectly acceptable to only execute standard RSpec tests in your modules and not use the extended RSpec Puppet matchers. If no Puppet module directories are identified during directory parsing, then no RSpec Puppet related actions (including those described below) will be performed.
Prior to executing the spec tests, Puppet Check will parse everything in the current path and identify all `spec` directories not within `fixtures` directories. It will then execute RSpec Puppet setup actions inside all directories one level above that contain a `manifests` directory. This is assumed to be a Puppet module directory. These setup actions include creating all of the necessary directories inside of `spec/fixtures`, creating a blank `site.pp` if it is missing, symlinking everything from the module that is needed into fixtures (automatically replaces functionality of self module symlink in `.fixtures.yaml` from Puppetlabs Spec Helper), and creates the `spec_helper.rb` if it is missing.
Puppet Check will also automatically download specified external module dependencies for and during RSpec Puppet testing. Currently `git`, `puppet forge`, and `hg` commands are supported. They can be implemented in the following way in your modules' `metadata.json`:
```json
"dependencies": [
{
"name": "module-name",
"forge": "forge-name"
},
{
"name": "module-name",
"git": "git-url"
},
{
"name": "module-name",
"hg": "hg-url"
}
]
```
Example:
```json
"dependencies": [
{
"name": "puppetlabs/stdlib",
"forge": "puppetlabs-stdlib"
},
{
"name": "puppetlabs/lvm",
"git": "https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-lvm.git"
}
]
```
#### puppetcheck:beaker
The spec tests will be executed against everything that matches the pattern `**/acceptance`. This means everything in the current path that appears to be a Puppet module acceptance test will be regarded as such and executed during this rake task.
Please note this is merely a frontend to Beaker and that Beaker itself has a self-contained scope compared to all the other tools Puppet Check interfaces with and utilizes. This means if you want to add Beaker-RSpec, Serverspec, etc., or perform advanced configurations, those would be all be performed within Beaker itself. This task merely provides an interface to integrate Beaker in with your other testing infrastructure.
### Exit Codes
- 0: PuppetCheck exited with no internal exceptions or errors in your Puppet code and data.
- 1: PuppetCheck exited with an internal exception (takes preference over other non-zero exit codes).
- 2: PuppetCheck exited with errors in your Puppet code and data.
### Optional dependencies
- **reek**: will automatically (with `bundler`, otherwise manually) be installed as a dependency and checks enabled during style checks if your Ruby version is `>= 2.1.0`.
- **rake**: install this if you want to use Puppet Check with `rake` tasks in addition to the CLI.
- **rspec**: install this if you want to use Puppet Check to execute the spec tests for your ruby files during `rake`.
- **rspec-puppet**: install this if you want to use Puppet Check to execute the spec tests for your Puppet files during `rake`.
- **beaker**: install this if you want to use Puppet Check to execute the acceptance tests during `rake`.
- **git**: install this if you want to use Puppet Check to download external module dependencies with `git` commands during RSpec Puppet testing.
- **mercurial**: install this if you want to use Puppet Check to download external module dependencies with `hg` commands during RSpec Puppet testing.
## Contributing
Code should pass all spec tests. New features should involve new spec tests. Adherence to Rubocop and Reek is expected where not overly onerous or where the check is of dubious cost/benefit.
A [Dockerfile](Dockerfile) is provided for easy rake testing. A [Vagrantfile](Vagrantfile) is provided for easy gem building, installation, and post-installation testing.
Please consult the [CHANGELOG](CHANGELOG.md) for the current development roadmap.