# GoogleAuthenticatorRails
[](http://badge.fury.io/rb/google-authenticator-rails)
[](http://travis-ci.org/jaredonline/google-authenticator)
[](https://codeclimate.com/github/jaredonline/google-authenticator)
Rails (ActiveRecord) integration with the Google Authenticator apps for [Android](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.google.android.apps.authenticator2) and the [iPhone](https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/google-authenticator/id388497605?mt=8). Uses the Authlogic style for cookie management.
## Installation
Add this line to your application's Gemfile:
gem 'google-authenticator-rails'
And then execute:
$ bundle
Or install it yourself as:
$ gem install google-authenticator-rails
## Usage
Example:
```ruby
class User
acts_as_google_authenticated
end
@user = User.new
@user.set_google_secret # => true
@user.google_qr_uri # => http://path.to.google/qr?with=params
@user.google_authentic?(123456) # => true
```
## Google Labels
When setting up an account with `GoogleAuthenticatorRails` you need to provide a label for that account (to distinguish it from other accounts).
`GoogleAuthenticatorRails` allows you to customize how the record will create that label. There are three options:
- The default just uses the column `email` on the model
- You can specify a custom column with the `:column_name` option
- You can specify a custom method via a symbol or a proc
Example:
```ruby
class User
acts_as_google_authenticated :column => :user_name
end
@user = User.new(:user_name => "ted")
@user.google_label # => "ted"
class User
acts_as_google_authenticated :method => :user_name_with_label
def user_name_with_label
"#{user_name}@example.com"
end
end
@user = User.new(:user_name => "ted")
@user.google_label # => "ted@example.com"
class User
acts_as_google_authenticated :method => Proc.new { |user| user.user_name_with_label.upcase }
def user_name_with_label
"#{user_name}@example.com"
end
end
@user = User.new(:user_name => "ted")
@user.google_label # => "TED@EXAMPLE.COM"
```
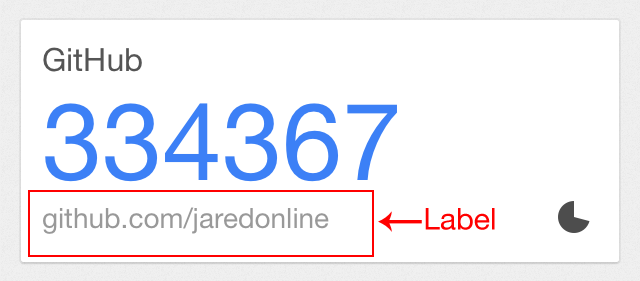
Here's what the labels look like in Google Authenticator for iPhone:
## Google Secret
The "google secret" is where `GoogleAuthenticatorRails` stores the
secret token used to generate the MFA code.
You can also specify a column for storing the google secret. The default is `google_secret`.
Example
```ruby
class User
acts_as_google_authenticated :google_secret_column => :mfa_secret
end
@user = User.new
@user.set_google_secret
@user.mfa_secret # => "56ahi483"
```
## Lookup Token
You can also specify which column the appropriate `MfaSession` subclass should use to look up the record:
Example
```ruby
class User
acts_as_google_authenticated :lookup_token => :salt
end
```
The above will cause the `UserMfaSession` class to call `User.where(:salt => cookie_salt)` or `User.scoped(:conditions => { :salt => cookie_salt })` to find the appropriate record.
### A note about record lookup
`GoogleAuthenticatorRails` makes one very large assumption when attempting to lookup a record. If your `MfaSession` subclass is named `UserMfaSession` it assumes you're trying to lookup a `User` record. Currently, there is no way to configure this, so if you're trying to lookup a `VeryLongModelNameForUser` you'll need to name your `MfaSession` subclass `VeryLongModelNameForUserMfaSession`.
For example:
```ruby
# app/models/user.rb
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
acts_as_google_authentic
end
# app/models/user_mfa_session.rb
class UserMfaSession < GoogleAuthenticatorRails::Session::Base
end
```
### A note about cookie creation and `Session::Persistence::TokenNotFound`
`GoogleAuthenticatorRails` looks up the record based on the cookie created when you call `MfaSession#create`. The `#create` method looks into the record class (in our example, `User`) and looks at the configured `:lookup_token` option. It uses that option to save two pieces of information into the cookie, the `id` of the record and the token, which defaults to `persistence_token`. `persistence_token` is what Authlogic uses, which this gem was originally designed to work with.
This can cause a lot of headaches if the model isn't configured correctly, and will cause a `GoogleAuthenticatorRails::Session::Persistence::TokenNotFound` error.
This error appears for one of three reasons:
1. `user` is `nil`
2. `user` doesn't respond to `:persistence_token`
3. `user.persistence_token` is blank
For example:
```ruby
# app/models/user.rb
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
acts_as_google_authentic
end
# Model has attributes:
# id: integer
# name: string
# salt: string
# app/models/user_mfa_session.rb
class UserMfaSession < GoogleAuthenticatorRails::Session::Base
end
# app/controllers/mfa_session_controller.rb
def class MfaSessionController < ApplicationController
def create
UserMfaSession.create(user) # => Error: GoogleAuthenticatorRails::Session::Persistence::TokenNotFound
end
end
```
The above example will fail because the `User` class doesn't have a `persistence_token` method. The fix for this is to configure `actions_as_google_authentic` to use the right column:
```ruby
# app/models/user.rb
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
acts_as_google_authentic :lookup_token => :salt
end
# Model has attributes:
# id: integer
# name: string
# salt: string
# app/models/user_mfa_session.rb
class UserMfaSession < GoogleAuthenticatorRails::Session::Base
end
# app/controllers/mfa_session_controller.rb
def class MfaSessionController < ApplicationController
def create
UserMfaSession.create(user)
end
end
```
This call to `#create` will succeed (as long as `user.salt` is not `nil`).
## Issuer
You can also specify a name for the 'issuer' (the name of the website) where the user is using this token:
Example
```ruby
class User
acts_as_google_authenticated :issuer => 'example.com'
end
```
This way your user will have the name of your site at the authenticator card besides the current token.
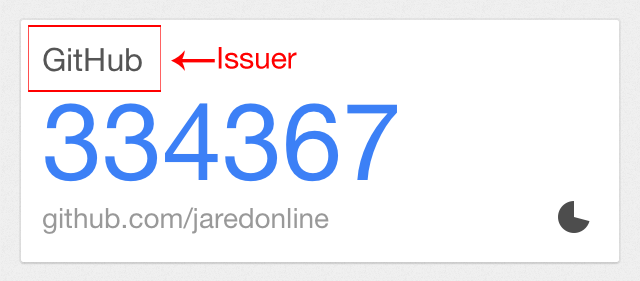
Here's what the issuers look like in Google Authenticator for iPhone:
## Sample Rails Setup
This is a very rough outline of how `GoogleAuthenticatorRails` is meant to manage the sessions and cookies for a Rails app.
```ruby
# Gemfile
gem 'rails'
gem 'google-authenticator-rails'
```
First add a field to your user model to hold the Google token.
```ruby
class AddGoogleSecretToUser < ActiveRecord::Migration
def change
add_column :users, :google_secret, :string
end
end
```
```ruby
# app/models/users.rb
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
acts_as_google_authenticated
end
```
If you want to authenticate based on a model called `User`, then you should name your session object `UserMfaSession`.
```ruby
# app/models/user_mfa_session.rb
class UserMfaSession < GoogleAuthenticatorRails::Session::Base
# no real code needed here
end
```
```ruby
# app/controllers/user_mfa_session_controller.rb
class UserMfaSessionController < ApplicationController
def new
# load your view
end
def create
user = current_user # grab your currently logged in user
if user.google_authentic?(params[:mfa_code])
UserMfaSession.create(user)
redirect_to root_path
else
flash[:error] = "Wrong code"
render :new
end
end
end
```
```ruby
# app/controllers/application_controller.rb
class ApplicationController < ActionController::Base
before_filter :check_mfa
private
def check_mfa
if !(user_mfa_session = UserMfaSession.find) && (user_mfa_session ? user_mfa_session.record == current_user : !user_mfa_session)
redirect_to new_user_mfa_session_path
end
end
end
```
## Other configuration
By default, the cookie related to the MfaSession expires in 24 hours, but this can be changed:
```ruby
# config/initializers/google_authenticator_rails.rb
GoogleAuthenticatorRails.time_until_expiration = 1.month
```
## Contributing
1. Fork it
2. Create your feature branch (`git checkout -b my-new-feature`)
3. Commit your changes (`git commit -am 'Added some feature'`)
4. Push to the branch (`git push origin my-new-feature`)
5. Create new Pull Request
## License
MIT.