# ActivityNotification
[](https://travis-ci.org/simukappu/activity_notification)
[](https://coveralls.io/github/simukappu/activity_notification?branch=master)
[](https://depfu.com/repos/simukappu/activity_notification)
[](http://inch-ci.org/github/simukappu/activity_notification)
[](https://rubygems.org/gems/activity_notification)
[](https://rubygems.org/gems/activity_notification)
[](MIT-LICENSE)
*activity_notification* provides integrated user activity notifications for Ruby on Rails. You can easily use it to configure multiple notification targets and make activity notifications with notifiable models, like adding comments, responding etc.
*activity_notification* supports Rails 4.2+ with ActiveRecord and [Mongoid](http://mongoid.org) ORM. It is tested for MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite3 with ActiveRecord and MongoDB with Mongoid.
## About
*activity_notification* provides following functions:
* Notification API (creating notifications, query for notifications and managing notification parameters)
* Notification models (stored with ActiveRecord or Mongoid ORM)
* Notification controllers (managing open/unopen of notifications, providing link to notifiable activity page)
* Notification views (presentation of notifications)
* Automatic tracked notifications (generating notifications along with the lifecycle of notifiable models)
* Grouping notifications (grouping like *"Kevin and 7 other users posted comments to this article"*)
* Email notification
* Batch email notification (event driven or periodical email notification, daily or weekly etc)
* Subscription management (subscribing and unsubscribing for each target and notification type)
* Integration with [Devise](https://github.com/plataformatec/devise) authentication
* Optional notification targets (Configurable optional notification targets like Amazon SNS, Slack, SMS and so on)
### Notification index and plugin notifications
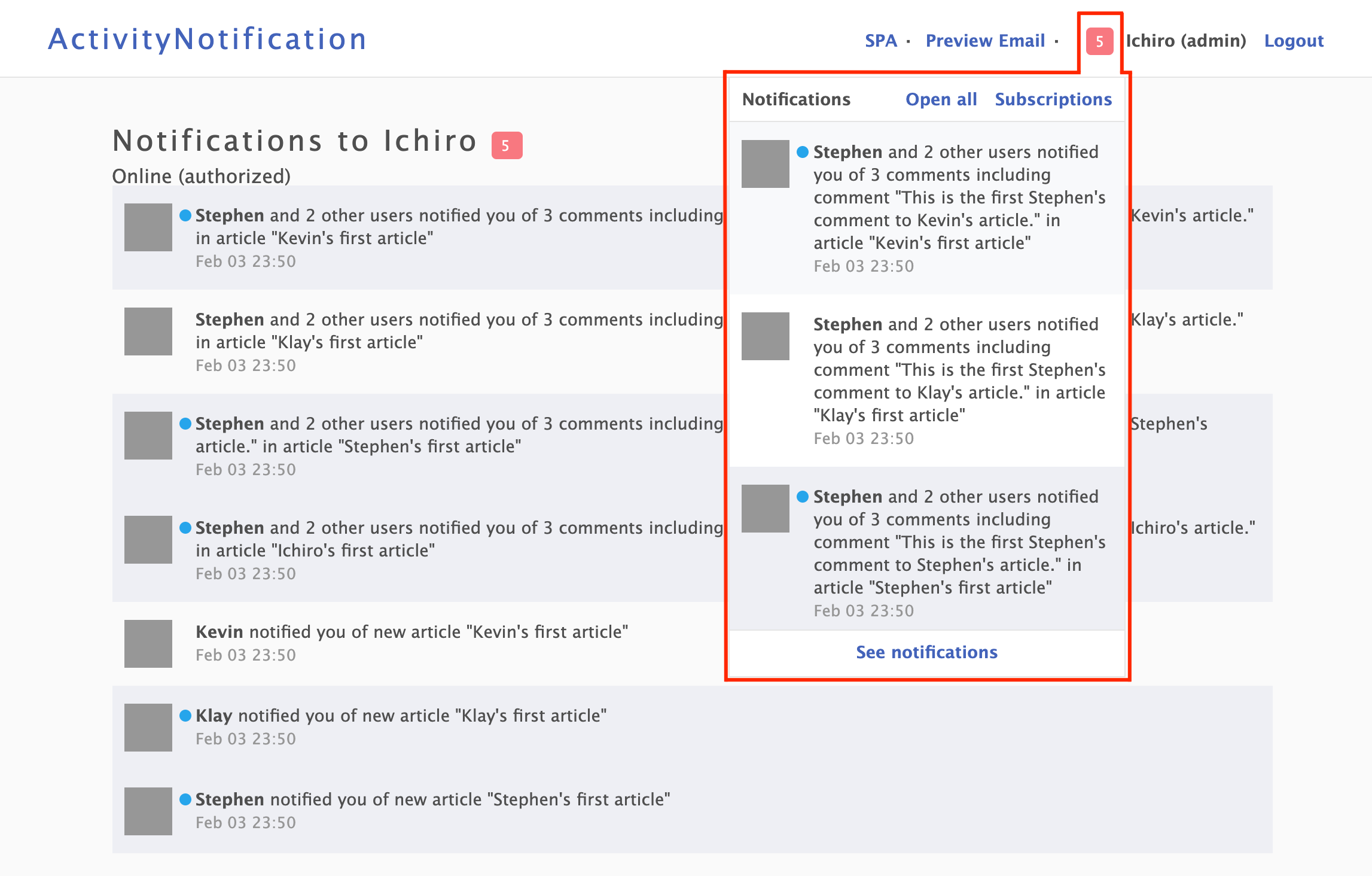
*activity_notification* deeply uses [PublicActivity](https://github.com/pokonski/public_activity) as reference in presentation layer.
### Subscription management of notifications
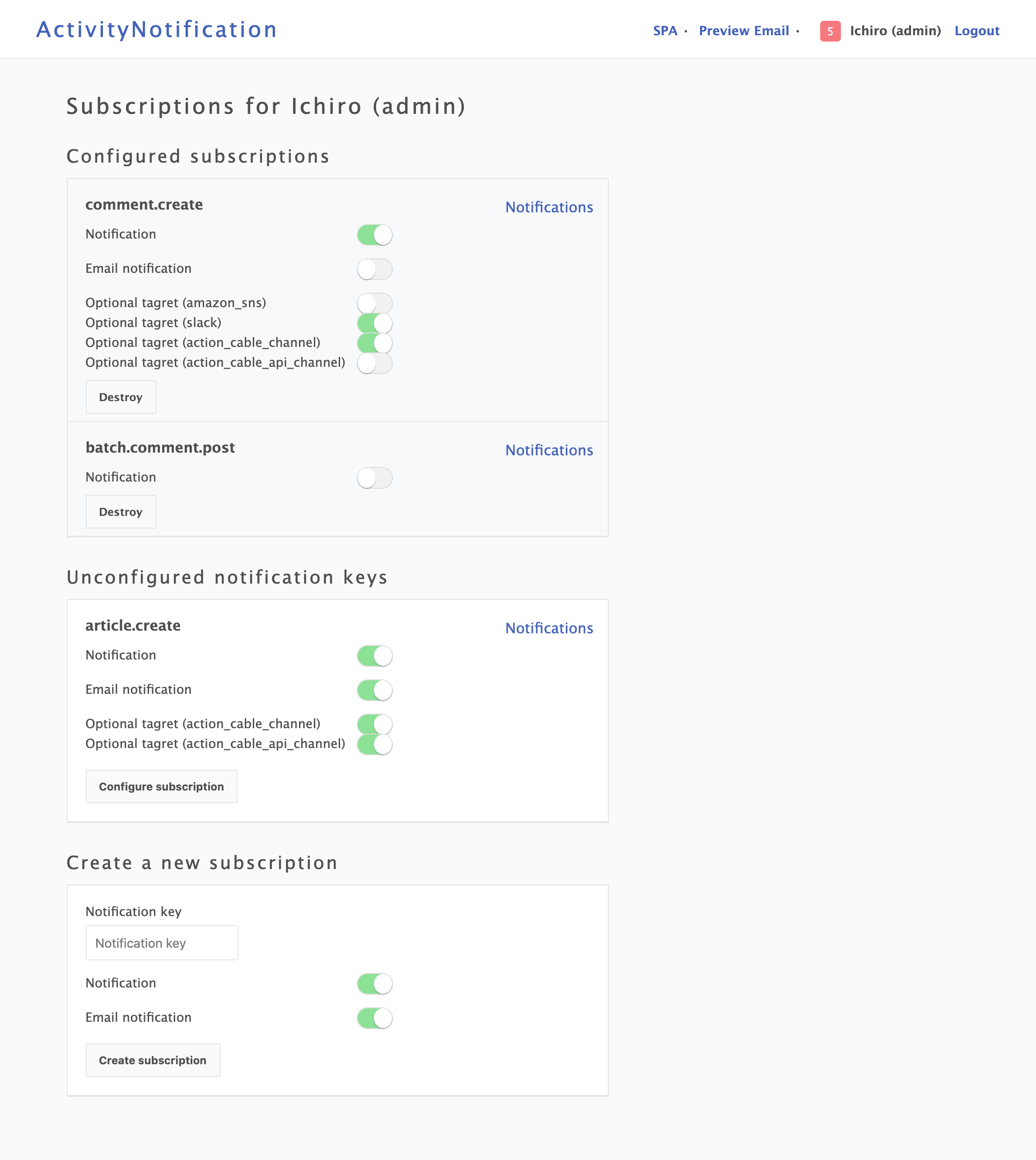
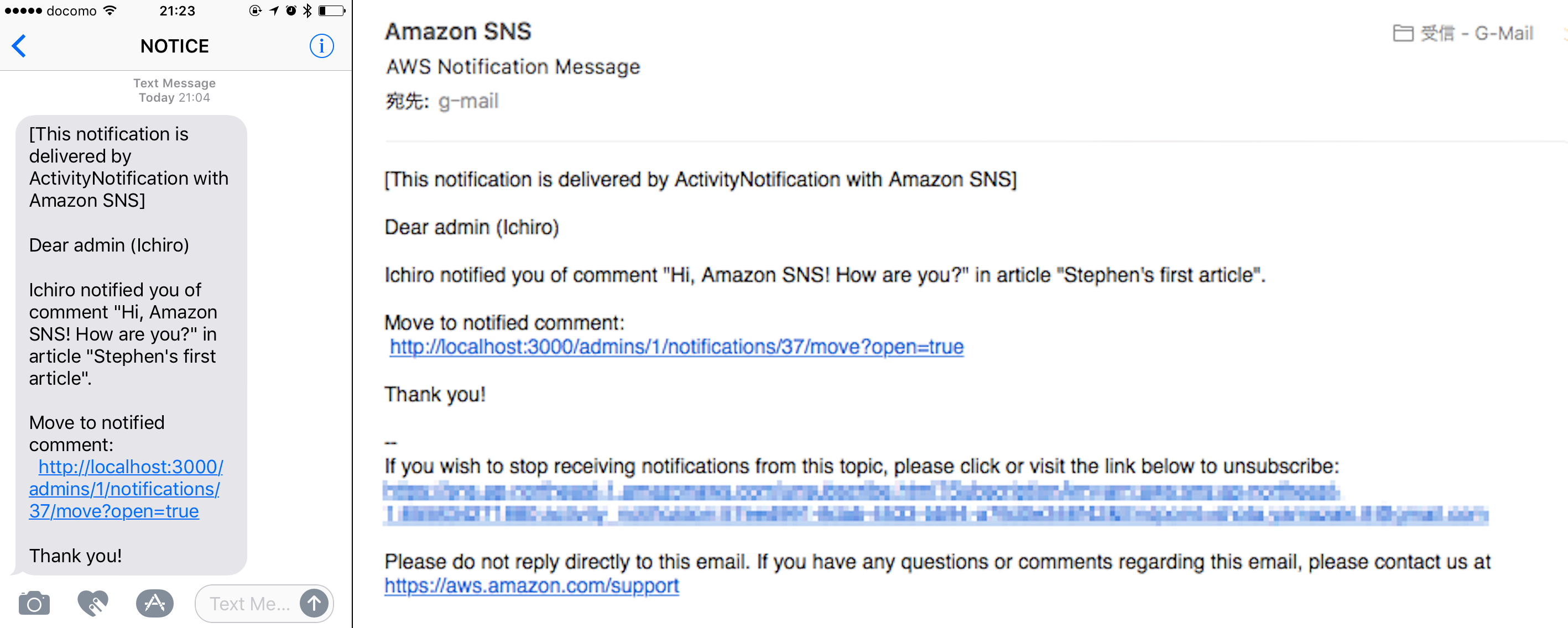
### Amazon SNS as optional notification target
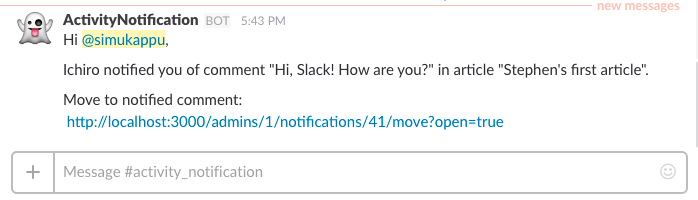
### Slack as optional notification target
## Table of contents
- [About](#about)
- [Setup](#setup)
- [Gem installation](#gem-installation)
- [Database setup](#database-setup)
- [Using ActiveRecord ORM](#using-activerecord-orm)
- [Using Mongoid ORM](#using-mongoid-orm)
- [Configuring models](#configuring-models)
- [Configuring target models](#configuring-target-models)
- [Configuring notifiable models](#configuring-notifiable-models)
- [Advanced notifiable path](#advanced-notifiable-path)
- [Configuring views](#configuring-views)
- [Configuring routes](#configuring-routes)
- [Routes with scope](#routes-with-scope)
- [Creating notifications](#creating-notifications)
- [Notification API](#notification-api)
- [Asynchronous notification API with ActiveJob](#asynchronous-notification-api-with-activejob)
- [Automatic tracked notifications](#automatic-tracked-notifications)
- [Displaying notifications](#displaying-notifications)
- [Preparing target notifications](#preparing-target-notifications)
- [Rendering notifications](#rendering-notifications)
- [Notification views](#notification-views)
- [i18n for notifications](#i18n-for-notifications)
- [Customizing controllers (optional)](#customizing-controllers-optional)
- [Functions](#functions)
- [Email notification](#email-notification)
- [Mailer setup](#mailer-setup)
- [Sender configuration](#sender-configuration)
- [Email templates](#email-templates)
- [Email subject](#email-subject)
- [i18n for email](#i18n-for-email)
- [Batch email notification](#batch-email-notification)
- [Batch mailer setup](#batch-mailer-setup)
- [Batch sender configuration](#batch-sender-configuration)
- [Batch email templates](#batch-email-templates)
- [Batch email subject](#batch-email-subject)
- [i18n for batch email](#i18n-for-batch-email)
- [Grouping notifications](#grouping-notifications)
- [Subscription management](#subscription-management)
- [Configuring subscriptions](#configuring-subscriptions)
- [Managing subscriptions](#managing-subscriptions)
- [Customizing subscriptions](#customizing-subscriptions)
- [Integration with Devise](#integration-with-devise)
- [Configuring integration with Devise](#configuring-integration-with-devise)
- [Using different model as target](#using-different-model-as-target)
- [Configuring simple default routes](#configuring-simple-default-routes)
- [Optional notification targets](#optional-notification-targets)
- [Configuring optional targets](#configuring-optional-targets)
- [Customizing message format](#customizing-message-format)
- [Amazon SNS as optional target](#amazon-sns-as-optional-target)
- [Slack as optional target](#slack-as-optional-target)
- [Developing custom optional targets](#developing-custom-optional-targets)
- [Testing](#testing)
- [Testing your application](#testing-your-application)
- [Testing gem alone](#testing-gem-alone)
- [Documentation](#documentation)
- **[Common examples](#common-examples)**
- [Help](#help)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
- [License](#license)
## Setup
### Gem installation
You can install *activity_notification* as you would any other gem:
```console
$ gem install activity_notification
```
or in your Gemfile:
```ruby
gem 'activity_notification'
```
After you install *activity_notification* and add it to your Gemfile, you need to run the generator:
```console
$ bin/rails generate activity_notification:install
```
The generator will install an initializer which describes all configuration options of *activity_notification*.
It also generates a i18n based translation file which we can configure the presentation of notifications.
### Database setup
#### Using ActiveRecord ORM
When you use *activity_notification* with ActiveRecord ORM as default configuration,
create migration for notifications and migrate the database in your Rails project:
```console
$ bin/rails generate activity_notification:migration
$ bin/rake db:migrate
```
If you are using a different table name from *"notifications"*, change the settings in your *config/initializers/activity_notification.rb* file, e.g., if you're using the table name *"activity_notifications"* instead of the default *"notifications"*:
```ruby
config.notification_table_name = "activity_notifications"
```
The same can be done for the subscription table name, e.g., if you're using the table name *"notifications_subscriptions"* instead of the default *"subscriptions"*:
```ruby
config.subscription_table_name = "notifications_subscriptions"
```
#### Using Mongoid ORM
When you use *activity_notification* with [Mongoid](http://mongoid.org) ORM, set **AN_ORM** environment variable to **mongoid**:
```console
$ export AN_ORM=mongoid
```
You can also configure ORM in initializer **activity_notification.rb**:
```ruby
config.orm = :mongoid
```
You need to configure Mongoid in your Rails application for your MongoDB environment. Then, your notifications and subscriptions will be stored in your MongoDB.
### Configuring models
#### Configuring target models
Configure your target model (e.g. *app/models/user.rb*).
Add **acts_as_target** configuration to your target model to get notifications.
##### Target as an ActiveRecord model
```ruby
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
# acts_as_target configures your model as ActivityNotification::Target
# with parameters as value or custom methods defined in your model as lambda or symbol.
# This is an example without any options (default configuration) as the target.
acts_as_target
end
```
##### Target as a Mongoid model
```ruby
require 'mongoid'
class User
include Mongoid::Document
include Mongoid::Timestamps
include GlobalID::Identification
# You need include ActivityNotification::Models except models which extend ActiveRecord::Base
include ActivityNotification::Models
acts_as_target
end
```
*Note*: *acts_as_notification_target* is an alias for *acts_as_target* and does the same.
#### Configuring notifiable models
Configure your notifiable model (e.g. *app/models/comment.rb*).
Add **acts_as_notifiable** configuration to your notifiable model representing activity to notify for each of your target model.
You have to define notification targets for all notifications from this notifiable model by *:targets* option. Other configurations are options. *:notifiable_path* option is a path to move when the notification is opened by the target user.
##### Notifiable as an ActiveRecord model
```ruby
class Article < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :user
has_many :comments, dependent: :destroy
has_many :commented_users, through: :comments, source: :user
end
class Comment < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :article
belongs_to :user
# acts_as_notifiable configures your model as ActivityNotification::Notifiable
# with parameters as value or custom methods defined in your model as lambda or symbol.
# The first argument is the plural symbol name of your target model.
acts_as_notifiable :users,
# Notification targets as :targets is a necessary option
# Set to notify to author and users commented to the article, except comment owner self
targets: ->(comment, key) {
([comment.article.user] + comment.article.commented_users.to_a - [comment.user]).uniq
},
# Path to move when the notification is opened by the target user
# This is an optional configuration since activity_notification uses polymorphic_path as default
notifiable_path: :article_notifiable_path
def article_notifiable_path
article_path(article)
end
end
```
##### Notifiable as a Mongoid model
```ruby
require 'mongoid'
class Article
include Mongoid::Document
include Mongoid::Timestamps
belongs_to :user
has_many :comments, dependent: :destroy
def commented_users
User.where(:id.in => comments.pluck(:user_id))
end
end
require 'mongoid'
class Comment
include Mongoid::Document
include Mongoid::Timestamps
include GlobalID::Identification
# You need include ActivityNotification::Models except models which extend ActiveRecord::Base
include ActivityNotification::Models
acts_as_notifiable :users,
targets: ->(comment, key) {
([comment.article.user] + comment.article.commented_users.to_a - [comment.user]).uniq
},
notifiable_path: :article_notifiable_path
def article_notifiable_path
article_path(article)
end
end
```
##### Advanced notifiable path
Sometimes it might be necessary to provide extra information in the *notifiable_path*. In those cases, passing a lambda function to the *notifiable_path* will give you the notifiable object and the notifiable key to play around with:
```ruby
acts_as_notifiable :users,
targets: ->(comment, key) {
([comment.article.user] + comment.article.commented_users.to_a - [comment.user]).uniq
},
notifiable_path: ->(comment, key) { "#{comment.article_notifiable_path}##{key}" }
```
This will attach the key of the notification to the notifiable path.
### Configuring views
*activity_notification* provides view templates to customize your notification views. The view generator can generate default views for all targets.
```console
$ bin/rails generate activity_notification:views
```
If you have multiple target models in your application, such as *User* and *Admin*, you will be able to have views based on the target like *notifications/users/index* and *notifications/admins/index*. If no view is found for the target, *activity_notification* will use the default view at *notifications/default/index*. You can also use the generator to generate views for the specified target:
```console
$ bin/rails generate activity_notification:views users
```
If you would like to generate only a few sets of views, like the ones for the *notifications* (for notification views) and *mailer* (for notification email views),
you can pass a list of modules to the generator with the *-v* flag.
```console
$ bin/rails generate activity_notification:views -v notifications
```
### Configuring routes
*activity_notification* also provides routing helper for notifications. Add **notify_to** method to *config/routes.rb* for the target (e.g. *:users*):
```ruby
Rails.application.routes.draw do
notify_to :users
end
```
Then, you can access several pages like */users/1/notifications* and manage open/unopen of notifications using **notifications_controller**.
If you use Devise integration and you want to configure simple default routes for authenticated users, see [Configuring simple default routes](#configuring-simple-default-routes).
#### Routes with scope
You can also configure *activity_notification* routes with scope like this:
```ruby
Rails.application.routes.draw do
scope :myscope, as: :myscope do
notify_to :users, routing_scope: :myscope
end
end
```
Then, pages are shown as */myscope/users/1/notifications*.
### Creating notifications
#### Notification API
You can trigger notifications by setting all your required parameters and triggering **notify** on the notifiable model, like this:
```ruby
@comment.notify :users, key: "comment.reply"
```
Or, you can call public API as **ActivityNotification::Notification.notify**
```ruby
ActivityNotification::Notification.notify :users, @comment, key: "comment.reply"
```
The first argument is the plural symbol name of your target model, which is configured in notifiable model by *acts_as_notifiable*.
The new instances of **ActivityNotification::Notification** model will be generated for the specified targets.
*Hint*: *:key* is a option. Default key `#{notifiable_type}.default` which means *comment.default* will be used without specified key.
You can override it by *Notifiable#default_notification_key*.
#### Asynchronous notification API with ActiveJob
Using Notification API with default configurations, the notifications will be generated synchronously. *activity_notification* also supports **asynchronous notification API** with ActiveJob to improve application performance. You can use **notify_later** method on the notifiable model, like this:
```ruby
@comment.notify_later :users, key: "comment.reply"
```
You can also use *:notify_later* option in *notify* method. This is the same operation as calling *notify_later* method.
```ruby
@comment.notify :users, key: "comment.reply", notify_later: true
```
*Note*: *notify_now* is an alias for *notify* and does the same.
When you use asynchronous notification API, you should setup ActiveJob with background queuing service such as Sidekiq.
You can set *config.active_job_queue* in your initializer to specify a queue name *activity_notification* will use.
The default queue name is *:activity_notification*.
```ruby
# Configure ActiveJob queue name for delayed notifications.
config.active_job_queue = :my_notification_queue
```
#### Automatic tracked notifications
You can also generate automatic tracked notifications by **:tracked** option in *acts_as_notifiable*.
*:tracked* option adds required callbacks to generate notifications for creation and update of the notifiable model.
Set true to *:tracked* option to generate all tracked notifications, like this:
```ruby
class Comment < ActiveRecord::Base
acts_as_notifiable :users,
targets: ->(comment, key) {
([comment.article.user] + comment.article.commented_users.to_a - [comment.user]).uniq
},
# Set true to :tracked option to generate automatic tracked notifications.
# It adds required callbacks to generate notifications for creation and update of the notifiable model.
tracked: true
end
```
Or, set *:only* or *:except* option to generate specified tracked notifications, like this:
```ruby
class Comment < ActiveRecord::Base
acts_as_notifiable :users,
targets: ->(comment, key) {
([comment.article.user] + comment.article.commented_users.to_a - [comment.user]).uniq
},
# Set { only: [:create] } to :tracked option to generate tracked notifications for creation only.
# It adds required callbacks to generate notifications for creation of the notifiable model.
tracked: { only: [:create] }
end
```
```ruby
class Comment < ActiveRecord::Base
acts_as_notifiable :users,
targets: ->(comment, key) {
([comment.article.user] + comment.article.commented_users.to_a - [comment.user]).uniq
},
# Set { except: [:update] } to :tracked option to generate tracked notifications except update (creation only).
# It adds required callbacks to generate notifications for creation of the notifiable model.
tracked: { except: [:update], key: 'comment.create.now', send_later: false }
end
```
*Hint*: `#{notifiable_type}.create` and `#{notifiable_type}.update` will be used as the key of tracked notifications.
You can override them by *Notifiable#notification_key_for_tracked_creation* and *Notifiable#notification_key_for_tracked_update*.
You can also specify key option in the *:tracked* statement.
As a default, the notifications will be generated synchronously along with model creation or update. If you want to generate notifications asynchronously, use *:notify_later* option with the *:tracked* option, like this:
```ruby
class Comment < ActiveRecord::Base
acts_as_notifiable :users,
targets: ->(comment, key) {
([comment.article.user] + comment.article.commented_users.to_a - [comment.user]).uniq
},
# It adds required callbacks to generate notifications asynchronously for creation of the notifiable model.
tracked: { only: [:create], key: 'comment.create.later', notify_later: true }
end
```
### Displaying notifications
#### Preparing target notifications
To display notifications, you can use **notifications** association of the target model:
```ruby
# custom_notifications_controller.rb
def index
@notifications = @target.notifications
end
```
You can also use several scope to filter notifications. For example, **unopened_only** to filter them unopened notifications only.
```ruby
# custom_notifications_controller.rb
def index
@notifications = @target.notifications.unopened_only
end
```
Moreover, you can use **notification_index** or **notification_index_with_attributes** methods to automatically prepare notification index for the target.
```ruby
# custom_notifications_controller.rb
def index
@notifications = @target.notification_index_with_attributes
end
```
#### Rendering notifications
You can use **render_notifications** helper in your views to show the notification index:
```erb
<%= render_notifications(@notifications) %>
```
We can set *:target* option to specify the target type of notifications:
```erb
<%= render_notifications(@notifications, target: :users) %>
```
*Note*: *render_notifications* is an alias for *render_notification* and does the same.
If you want to set notification index in the common layout, such as common header, you can use **render_notifications_of** helper like this:
```shared/_header.html.erb
<%= render_notifications_of current_user, index_content: :with_attributes %>
```
Then, content named **:notification_index** will be prepared and you can use it in your partial template.
```activity_notifications/notifications/users/_index.html.erb
...
<%= yield :notification_index %>
...
```
Sometimes, it's desirable to pass additional local variables to partials. It can be done this way:
```erb
<%= render_notification(@notification, locals: { friends: current_user.friends }) %>
```
#### Notification views
*activity_notification* looks for views in *app/views/activity_notification/notifications/:target* with **:key** of the notifications.
For example, if you have a notification with *:key* set to *"notification.comment.reply"* and rendered it with *:target* set to *:users*, the gem will look for a partial in *app/views/activity_notification/notifications/users/comment/_reply.html.(|erb|haml|slim|something_else)*.
*Hint*: the *"notification."* prefix in *:key* is completely optional, you can skip it in your projects or use this prefix only to make namespace.
If you would like to fallback to a partial, you can utilize the **:fallback** parameter to specify the path of a partial to use when one is missing:
```erb
<%= render_notification(@notification, target: :users, fallback: :default) %>
```
When used in this manner, if a partial with the specified *:key* cannot be located, it will use the partial defined in the *:fallback* instead. In the example above this would resolve to *activity_notification/notifications/users/_default.html.(|erb|haml|slim|something_else)*.
If you do not specify *:target* option like this,
```erb
<%= render_notification(@notification, fallback: :default) %>
```
the gem will look for a partial in *default* as the target type which means *activity_notification/notifications/default/_default.html.(|erb|haml|slim|something_else)*.
If a view file does not exist then *ActionView::MisingTemplate* will be raised. If you wish to fallback to the old behaviour and use an i18n based translation in this situation you can specify a *:fallback* parameter of *:text* to fallback to this mechanism like such:
```erb
<%= render_notification(@notification, fallback: :text) %>
```
Finally, default views of *activity_notification* depends on jQuery and you have to add requirements to *application.js* in your apps:
```app/assets/javascripts/application.js
//= require jquery
//= require jquery_ujs
```
#### i18n for notifications
Translations are used by the *#text* method, to which you can pass additional options in form of a hash. *#render* method uses translations when view templates have not been provided. You can render pure i18n strings by passing `{ i18n: true }` to *#render_notification* or *#render*.
Translations should be put in your locale *.yml* files as **text** field. To render pure strings from I18n example structure:
```yaml
notification:
user:
article:
create:
text: 'Article has been created'
update:
text: 'Article %{article_title} has been updated'
destroy:
text: 'Some user removed an article!'
comment:
post:
text:
one: "%{notifier_name} posted a comment on your article %{article_title}
"
other: "%{notifier_name} posted %{count} comments on your article %{article_title}
"
reply:
text: "%{notifier_name} and %{group_member_count} other people replied %{group_notification_count} times to your comment
"
mail_subject: 'New comment on your article'
admin:
article:
post:
text: '[Admin] Article has been created'
```
This structure is valid for notifications with keys *"notification.comment.reply"* or *"comment.reply"*. As mentioned before, *"notification."* part of the key is optional. In addition for above example, `%{notifier_name}` and `%{article_title}` are used from parameter field in the notification record. Pluralization is supported (but optional) for grouped notifications using the `%{group_notification_count}` value.
### Customizing controllers (optional)
If the customization at the views level is not enough, you can customize each controller by following these steps:
1. Create your custom controllers using the generator with a target:
```console
$ bin/rails generate activity_notification:controllers users
```
If you specify *users* as the target, controllers will be created in *app/controllers/users*.
And the notifications controller will look like this:
```ruby
class Users::NotificationsController < ActivityNotification::NotificationsController
# GET /:target_type/:target_id/notifications
# def index
# super
# end
# ...
# POST /:target_type/:target_id/notifications/:id/open
# def open
# super
# end
# ...
end
```
2. Tell the router to use this controller:
```ruby
notify_to :users, controller: 'users/notifications'
```
3. Finally, change or extend the desired controller actions.
You can completely override a controller action
```ruby
class Users::NotificationsController < ActivityNotification::NotificationsController
# ...
# POST /:target_type/:target_id/notifications/:id/open
def open
# Custom code to open notification here
# super
end
# ...
end
```
## Functions
### Email notification
*activity_notification* provides email notification to the notification targets.
#### Mailer setup
Set up SMTP server configuration for *ActionMailer*. Then, you need to set up the default URL options for the *activity_notification* mailer in each environment. Here is a possible configuration for *config/environments/development.rb*:
```ruby
config.action_mailer.default_url_options = { host: 'localhost', port: 3000 }
```
Email notification is disabled as default. You can configure to enable email notification in initializer *activity_notification.rb*.
```ruby
config.email_enabled = true
```
You can also configure them for each model by *acts_as roles* like these.
```ruby
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
# Example using confirmed_at of devise field
# to decide whether activity_notification sends notification email to this user
acts_as_target email: :email, email_allowed: :confirmed_at
end
```
```ruby
class Comment < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :article
belongs_to :user
acts_as_notifiable :users,
targets: ->(comment, key) {
([comment.article.user] + comment.article.commented_users.to_a - [comment.user]).uniq
},
# Allow notification email
email_allowed: true,
notifiable_path: :article_notifiable_path
def article_notifiable_path
article_path(article)
end
end
```
#### Sender configuration
You can configure the notification *"from"* address inside of *activity_notification.rb* in two ways.
Using a simple email address as *String*:
```ruby
config.mailer_sender = 'your_notification_sender@example.com'
```
Using a *Proc* to configure the sender based on the *notification.key*:
```ruby
config.mailer_sender = ->(key){ key == 'inquiry.post' ? 'support@example.com' : 'noreply@example.com' }
```
#### Email templates
*activity_notification* will look for email template in the same way as notification views. For example, if you have a notification with *:key* set to *"notification.comment.reply"* and target_type *users*, the gem will look for a partial in *app/views/activity_notification/mailer/users/comment/_reply.html.(|erb|haml|slim|something_else)*.
If this template is missing, the gem will look for a partial in *default* as the target type which means *activity_notification/mailer/default/_default.html.(|erb|haml|slim|something_else)*.
#### Email subject
*activity_notification* will use `"Notification of #{@notification.notifiable.printable_type.downcase}"` as default email subject. If it is defined, *activity_notification* will resolve email subject from *overriding_notification_email_subject* method in notifiable models. You can customize email subject like this:
```
class Comment < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :article
belongs_to :user
acts_as_notifiable :users,
targets: ->(comment, key) {
([comment.article.user] + comment.article.commented_users.to_a - [comment.user]).uniq
},
notifiable_path: :article_notifiable_path
def overriding_notification_email_subject(target, key)
if key == "comment.create"
"New comment to your article!"
else
"Notification for new comments!"
end
end
end
```
If you use i18n for email, you can configure email subject in your locale files. See [i18n for email](#i18n-for-email).
#### i18n for email
The subject of notification email can be put in your locale *.yml* files as **mail_subject** field:
```yaml
notification:
user:
comment:
post:
text: "Someone posted comments to your article
"
mail_subject: 'New comment to your article'
```
### Batch email notification
*activity_notification* provides batch email notification to the notification targets. You can send notification email daily, hourly or weekly and so on with a scheduler like *whenever*.
#### Batch mailer setup
Set up SMTP server configuration for *ActionMailer* and the default URL options for the *activity_notification* mailer in each environment.
Batch email notification is disabled as default. You can configure to enable email notification in initializer *activity_notification.rb* like single email notification.
```ruby
config.email_enabled = true
```
You can also configure them for each target model by *acts_as_target* role like this.
```ruby
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
# Example using confirmed_at of devise field
# to decide whether activity_notification sends batch notification email to this user
acts_as_target email: :email, batch_email_allowed: :confirmed_at
end
```
Then, you can send batch notification email for unopened notifications only to the all specified targets with *batch_key*.
```ruby
# Send batch notification email to the users with unopened notifications
User.send_batch_unopened_notification_email(batch_key: 'batch.comment.post')
```
You can also add conditions to filter notifications, like this:
```ruby
# Send batch notification email to the users with unopened notifications of specified key in 1 hour
User.send_batch_unopened_notification_email(batch_key: 'batch.comment.post', filtered_by_key: 'comment.post', custom_filter: ["created_at >= ?", time.hour.ago])
```
#### Batch sender configuration
*activity_notification* uses same sender configuration of real-time email notification as batch email sender.
You can configure *config.mailer_sender* as simply *String* or *Proc* based on the *batch_key*:
```ruby
config.mailer_sender = ->(batch_key){ batch_key == 'batch.inquiry.post' ? 'support@example.com' : 'noreply@example.com' }
```
*batch_key* is specified by **:batch_key** option. If this option is not specified, the key of the first notification will be used as *batch_key*.
#### Batch email templates
*activity_notification* will look for batch email template in the same way as email notification using *batch_key*.
#### Batch email subject
*activity_notification* will resolve batch email subject as the same way as [email subject](#email-subject) with *batch_key*.
If you use i18n for batch email, you can configure batch email subject in your locale files. See [i18n for batch email](#i18n-for-batch-email).
#### i18n for batch email
The subject of batch notification email also can be put in your locale *.yml* files as **mail_subject** field for *batch_key*.
```yaml
notification:
user:
batch:
comment:
post:
mail_subject: 'New comments to your article'
```
### Grouping notifications
*activity_notification* provides the function for automatically grouping notifications. When you created a notification like this, all *unopened* notifications to the same target will be grouped by *article* set as **:group** options:
```ruby
@comment.notify :users key: 'comment.post', group: @comment.article
```
When you use default notification view, it is helpful to configure **acts_as_notification_group** (or *acts_as_group*) with *:printable_name* option to render group instance.
```ruby
class Article < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :user
acts_as_notification_group printable_name: ->(article) { "article \"#{article.title}\"" }
end
```
You can use **group_owners_only** scope to filter owner notifications representing each group:
```ruby
# custom_notifications_controller.rb
def index
@notifications = @target.notifications.group_owners_only
end
```
*notification_index* and *notification_index_with_attributes* methods also use *group_owners_only* scope internally.
And you can render them in a view like this:
```erb
<% if notification.group_member_exists? %>
<%= "#{notification.notifier.name} and #{notification.group_member_count} other users" %>
<% else %>
<%= "#{notification.notifier.name}" %>
<% end %>
<%= "posted comments to your article \"#{notification.group.title}\"" %>
```
This presentation will be shown to target users as *Kevin and 7 other users posted comments to your article "Let's use Ruby"*.
You can also use `%{group_member_count}`, `%{group_notification_count}`, `%{group_member_notifier_count}` and `%{group_notifier_count}` in i18n text as a field:
```yaml
notification:
user:
comment:
post:
text: "%{notifier_name} and %{group_member_notifier_count} other users posted %{group_notification_count} comments to your article
"
mail_subject: 'New comment to your article'
```
Then, you will see *"Kevin and 7 other users posted 10 comments to your article"*.
### Subscription management
*activity_notification* provides the function for subscription management of notifications and notification email.
#### Configuring subscriptions
Subscription management is disabled as default. You can configure to enable subscription management in initializer *activity_notification.rb*.
```ruby
config.subscription_enabled = true
```
This makes all target model subscribers. You can also configure them for each target model by *acts_as_target* role like this.
```ruby
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
# Example using confirmed_at of devise field
# to decide whether activity_notification manages subscriptions of this user
acts_as_target email: :email, email_allowed: :confirmed_at, subscription_allowed: :confirmed_at
end
```
If you do not have a subscriptions table in you database, create a migration for subscriptions and migrate the database in your Rails project:
```console
$ bin/rails generate activity_notification:migration CreateSubscriptions -t subscriptions
$ bin/rake db:migrate
```
If you are using a different table name than the default "subscriptions", change the settings in your config/initializers/activity_notification.rb file, e.g, if you use the table name "notifications_subscription" instead:
```
config.subscription_table_name = "notifications_subscriptions"
```
#### Managing subscriptions
Subscriptions are managed by instances of **ActivityNotification::Subscription** model which belongs to *target* and *key* of the notification.
*Subscription#subscribing* manages subscription of notifications.
*true* means the target will receive the notifications with this key.
*false* means the target will not receive these notifications.
*Subscription#subscribing_to_email* manages subscription of notification email.
*true* means the target will receive the notification email with this key including batch notification email with this *batch_key*.
*false* means the target will not receive these notification email.
As default, all target subscribes to notification and notification email when subscription record does not exist in your database.
You can change this **subscribe_as_default** parameter in initializer *activity_notification.rb*.
```ruby
config.subscribe_as_default = false
```
Then, all target does not subscribe to notification and notification email and will not receive any notifications as default.
You can create subscription record from subscription API in your target model like this:
```ruby
# Subscribe 'comment.reply' notifications and notification email
user.create_subscription(key: 'comment.reply')
# Subscribe 'comment.reply' notifications but does not subscribe notification email
user.create_subscription(key: 'comment.reply', subscribing_to_email: false)
# Unsubscribe 'comment.reply' notifications and notification email
user.create_subscription(key: 'comment.reply', subscribing: false)
```
You can also update subscriptions like this:
```ruby
# Subscribe 'comment.reply' notifications and notification email
user.find_or_create_subscription('comment.reply').subscribe
# Unsubscribe 'comment.reply' notifications and notification email
user.find_or_create_subscription('comment.reply').unsubscribe
# Unsubscribe 'comment.reply' notification email
user.find_or_create_subscription('comment.reply').unsubscribe_to_email
```
#### Customizing subscriptions
*activity_notification* provides basic controllers and views to manage the subscriptions.
Add subscription routing to *config/routes.rb* for the target (e.g. *:users*):
```ruby
Rails.application.routes.draw do
subscribed_by :users
end
```
or, you can also configure it with notifications like this:
```ruby
Rails.application.routes.draw do
notify_to :users, with_subscription: true
end
```
Then, you can access *users/1/subscriptions* and use **subscriptions_controller** or **subscriptions_with_devise_controller** to manage the subscriptions.
If you would like to customize subscription controllers or views, you can use generators like notifications:
* Customize subscription controllers
1. Create your custom controllers using controller generator with a target:
```console
$ bin/rails generate activity_notification:controllers users -c subscriptions subscriptions_with_devise
```
2. Tell the router to use this controller:
```ruby
notify_to :users, with_subscription: { controller: 'users/subscriptions' }
```
* Customize subscription views
```console
$ bin/rails generate activity_notification:views users -v subscriptions
```
### Integration with Devise
*activity_notification* supports to integrate with devise authentication.
#### Configuring integration with Devise
Add **:with_devise** option in notification routing to *config/routes.rb* for the target:
```ruby
Rails.application.routes.draw do
devise_for :users
# Integrated with devise
notify_to :users, with_devise: :users
end
```
Then *activity_notification* will use **notifications_with_devise_controller** as a notification controller. The controller actions automatically call *authenticate_user!* and the user will be restricted to access and operate own notifications only, not others'.
*Hint*: HTTP 403 Forbidden will be returned for unauthorized notifications.
#### Using different model as target
You can also use different model from Devise resource as a target. When you will add this to *config/routes.rb*:
```ruby
Rails.application.routes.draw do
devise_for :users
# Integrated with devise for different model
notify_to :admins, with_devise: :users
end
```
and add **:devise_resource** option to *acts_as_target* in the target model:
```ruby
class Admin < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :user
acts_as_target devise_resource: :user
end
```
*activity_notification* will authenticate *:admins* notifications with devise authentication for *:users*.
In this example, *activity_notification* will confirm *admin* belonging to authenticated *user* by Devise.
#### Configuring simple default routes
You can configure simple default routes for authenticated users, like */notifications* instead of */users/1/notifications*. Use *:devise_default_routes* option like this:
```ruby
Rails.application.routes.draw do
devise_for :users
notify_to :users, with_devise: :users, devise_default_routes: true
end
```
If you use multiple notification targets with Devise, you can also use this option with scope like this:
```ruby
Rails.application.routes.draw do
devise_for :users
# Integrated with devise for different model, and use with scope
scope :admins, as: :admins do
notify_to :admins, with_devise: :users, devise_default_routes: true, routing_scope: :admins
end
end
```
Then, you can access */admins/notifications* instead of */admins/1/notifications*.
### Optional notification targets
*activity_notification* supports configurable optional notification targets like Amazon SNS, Slack, SMS and so on.
#### Configuring optional targets
*activity_notification* provides default optional target implementation for Amazon SNS and Slack.
You can develop any optional target classes which extends *ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::Base*, and configure them to notifiable model by *acts_as_notifiable* like this.
```ruby
class Comment < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :article
belongs_to :user
require 'activity_notification/optional_targets/amazon_sns'
require 'activity_notification/optional_targets/slack'
require 'custom_optional_targets/console_output'
acts_as_notifiable :admins, targets: [Admin.first].compact,
notifiable_path: :article_notifiable_path,
# Set optional target implementation class and initializing parameters
optional_targets: {
ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::AmazonSNS => { topic_arn: 'arn:aws:sns:XXXXX:XXXXXXXXXXXX:XXXXX' },
ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::Slack => {
webhook_url: 'https://hooks.slack.com/services/XXXXXXXXX/XXXXXXXXX/XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX',
slack_name: :slack_name, channel: 'activity_notification', username: 'ActivityNotification', icon_emoji: ":ghost:"
},
CustomOptionalTarget::ConsoleOutput => {}
}
def article_notifiable_path
article_path(article)
end
end
```
Write *require* statement for optional target implementation classes and set them with initializing parameters to *acts_as_notifiable*.
*activity_notification* will publish all notifications of those targets and notifiables to optional targets.
#### Customizing message format
Optional targets prepare publishing messages from notification instance using view template like rendering notifications.
As default, all optional targets use *app/views/activity_notification/optional_targets/default/base/_default.text.erb*.
You can customize this template by creating *app/views/activity_notification/optional_targets///.text.(|erb|haml|slim|something_else)*.
For example, if you have a notification for *:users* target with *:key* set to *"notification.comment.reply"* and *ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::AmazonSNS* optional target is configured, the gem will look for a partial in *app/views/activity_notification/optional_targets/users/amazon_sns/comment/_reply.text.erb*.
The gem will also look for templates whose ** is *default*, ** is *base* and ** is *default*, which means *app/views/activity_notification/optional_targets/users/amazon_sns/_default.text.erb*, *app/views/activity_notification/optional_targets/users/base/_default.text.erb*, *app/views/activity_notification/optional_targets/default/amazon_sns/_default.text.erb* and *app/views/activity_notification/optional_targets/default/base/_default.text.erb*.
#### Amazon SNS as optional target
*activity_notification* provides **ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::AmazonSNS** as default optional target implementation for Amazon SNS.
First, add **aws-sdk** or **aws-sdk-sns** (>= AWS SDK for Ruby v3) gem to your Gemfile and set AWS Credentials for SDK (See [Configuring the AWS SDK for Ruby](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sdk-for-ruby/v3/developer-guide/setup-config.html)).
```ruby
gem 'aws-sdk', '~> 2'
# --- or ---
gem 'aws-sdk-sns', '~> 1'
```
```ruby
require 'aws-sdk'
# --- or ---
require 'aws-sdk-sns'
Aws.config.update(
region: 'your_region',
credentials: Aws::Credentials.new('your_access_key_id', 'your_secret_access_key')
)
```
Then, write `require 'activity_notification/optional_targets/amazon_sns'` statement in your notifiable model and set *ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::AmazonSNS* to *acts_as_notifiable* with *:topic_arn*, *:target_arn* or *:phone_number* initializing parameters.
Any other options for `Aws::SNS::Client.new` are available as initializing parameters. See [API Reference of Class: Aws::SNS::Client](http://docs.aws.amazon.com/sdk-for-ruby/v3/api/Aws/SNS/Client.html) for more details.
```ruby
class Comment < ActiveRecord::Base
require 'activity_notification/optional_targets/amazon_sns'
acts_as_notifiable :admins, targets: [Admin.first].compact,
optional_targets: {
ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::AmazonSNS => { topic_arn: 'arn:aws:sns:XXXXX:XXXXXXXXXXXX:XXXXX' }
}
end
```
#### Slack as optional target
*activity_notification* provides **ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::Slack** as default optional target implementation for Slack.
First, add **slack-notifier** gem to your Gemfile and create Incoming WebHooks in Slack (See [Incoming WebHooks](https://wemakejp.slack.com/apps/A0F7XDUAZ-incoming-webhooks)).
```ruby
gem 'slack-notifier'
```
Then, write `require 'activity_notification/optional_targets/slack'` statement in your notifiable model and set *ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::Slack* to *acts_as_notifiable* with *:webhook_url* and *:target_username* initializing parameters. *:webhook_url* is created WebHook URL and required, *:target_username* is target's slack user name as String value, symbol method name or lambda function and is optional.
Any other options for `Slack::Notifier.new` are available as initializing parameters. See [Github slack-notifier](https://github.com/stevenosloan/slack-notifier) and [API Reference of Class: Slack::Notifier](http://www.rubydoc.info/gems/slack-notifier/1.5.1/Slack/Notifier) for more details.
```ruby
class Comment < ActiveRecord::Base
require 'activity_notification/optional_targets/slack'
acts_as_notifiable :admins, targets: [Admin.first].compact,
optional_targets: {
ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::Slack => {
webhook_url: 'https://hooks.slack.com/services/XXXXXXXXX/XXXXXXXXX/XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX',
target_username: :slack_username, channel: 'activity_notification', username: 'ActivityNotification', icon_emoji: ":ghost:"
}
}
end
```
#### Developing custom optional targets
You can develop any custom optional targets.
Custom optional target class must extend **ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::Base** and override **initialize_target** and **notify** method.
You can use **render_notification_message** method to prepare message from notification instance using view template.
For example, create *lib/custom_optional_targets/amazon_sns.rb* as follows:
```ruby
module CustomOptionalTarget
# Custom optional target implementation for mobile push notification or SMS using Amazon SNS.
class AmazonSNS < ActivityNotification::OptionalTarget::Base
require 'aws-sdk'
# Initialize method to prepare Aws::SNS::Client
def initialize_target(options = {})
@topic_arn = options.delete(:topic_arn)
@target_arn = options.delete(:target_arn)
@phone_number = options.delete(:phone_number)
@sns_client = Aws::SNS::Client.new(options)
end
# Publishes notification message to Amazon SNS
def notify(notification, options = {})
@sns_client.publish(
topic_arn: notification.target.resolve_value(options.delete(:topic_arn) || @topic_arn),
target_arn: notification.target.resolve_value(options.delete(:target_arn) || @target_arn),
phone_number: notification.target.resolve_value(options.delete(:phone_number) || @phone_number),
message: render_notification_message(notification, options)
)
end
end
end
```
Then, you can configure them to notifiable model by *acts_as_notifiable* like this.
```ruby
class Comment < ActiveRecord::Base
require 'custom_optional_targets/amazon_sns'
acts_as_notifiable :admins, targets: [Admin.first].compact,
optional_targets: {
CustomOptionalTarget::AmazonSNS => { topic_arn: 'arn:aws:sns:XXXXX:XXXXXXXXXXXX:XXXXX' }
}
end
```
*acts_as_notifiable* creates optional target instances and calls *initialize_target* method with initializing parameters.
## Testing
### Testing your application
First, you need to configure ActivityNotification as described above.
#### Testing notifications with RSpec
Prepare target and notifiable model instances to test generating notifications (e.g. `@user` and `@comment`).
Then, you can call notify API and test if notifications of the target are generated.
```ruby
# Prepare
@article_author = create(:user)
@comment = @article_author.articles.create.comments.create
expect(@article_author.notifications.unopened_only.count).to eq(0)
# Call notify API
@comment.notify :users
# Test generated notifications
expect(@article_author_user.notifications.unopened_only.count).to eq(1)
expect(@article_author_user.notifications.unopened_only.latest.notifiable).to eq(@comment)
```
#### Testing email notifications with RSpec
Prepare target and notifiable model instances to test sending notification email.
Then, you can call notify API and test if notification email is sent.
```ruby
# Prepare
@article_author = create(:user)
@comment = @article_author.articles.create.comments.create
expect(ActivityNotification::Mailer.deliveries.size).to eq(0)
# Call notify API and send email now
@comment.notify :users, send_later: false
# Test sent notification email
expect(ActivityNotification::Mailer.deliveries.size).to eq(1)
expect(ActivityNotification::Mailer.deliveries.first.to[0]).to eq(@article_author.email)
```
Note that notification email will be sent asynchronously without false as *:send_later* option.
```ruby
# Prepare
include ActiveJob::TestHelper
@article_author = create(:user)
@comment = @article_author.articles.create.comments.create
expect(ActivityNotification::Mailer.deliveries.size).to eq(0)
# Call notify API and send email asynchronously as default
# Test sent notification email with ActiveJob queue
expect {
perform_enqueued_jobs do
@comment.notify :users
end
}.to change { ActivityNotification::Mailer.deliveries.size }.by(1)
expect(ActivityNotification::Mailer.deliveries.first.to[0]).to eq(@article_author.email)
```
### Testing gem alone
#### Testing with RSpec
Pull git repository and execute RSpec.
```console
$ git pull https://github.com/simukappu/activity_notification.git
$ cd activity_notification
$ bundle install —path vendor/bundle
$ bundle exec rspec
- or -
$ bundle exec rake
```
#### Dummy Rails application
Test module includes dummy Rails application in **spec/rails_app**. You can run the dummy application as common Rails application.
```console
$ cd spec/rails_app
$ bin/rake db:migrate
$ bin/rake db:seed
$ bin/rails server
```
Then, you can access for the dummy application.
##### Run with your local database
As default, dummy Rails application runs with local SQLite database in *spec/rails_app/db/development.sqlite3*.
This application supports to run with your local MySQL, PostgreSQL and MongoDB.
Set **AN_TEST_DB** environment variable like:
```console
$ export AN_TEST_DB=mysql
```
for MySQL,
```console
$ export AN_TEST_DB=postgresql
```
for PostgreSQL, and
```console
$ export AN_TEST_DB=mongodb
```
for MongoDB. When you set **mongodb** as *AN_TEST_DB*, you have to use *activity_notification* with MongoDB. Also set **AN_ORM** like:
```console
$ export AN_ORM=mongoid
```
Then, configure *spec/rails_app/config/database.yml* or *spec/rails_app/config/mongoid.yml* as your local database.
Finally, run database migration, seed data script and the dummy appliation.
```console
$ cd spec/rails_app
$ # You don't need migration when you use MongoDB only (AN_ORM=mongoid and AN_TEST_DB=mongodb)
$ bin/rake db:migrate
$ bin/rake db:seed
$ bin/rails server
```
## Documentation
See [API Reference](http://www.rubydoc.info/github/simukappu/activity_notification/index) for more details.
RubyDoc.info does not support parsing methods in *included* and *class_methods* of *ActiveSupport::Concern* currently.
To read complete documents, please generate YARD documents on your local environment:
```console
$ git pull https://github.com/simukappu/activity_notification.git
$ cd activity_notification
$ bundle install —path vendor/bundle
$ bundle exec yard doc
$ bundle exec yard server
```
Then you can see the documents at .
## Common examples
To be prepared. See dummy Rails application in *spec/rails_app*.
## Help
We are welcome your Github issues for gem problems or enhancement requests. If you have any questions or problems for your own application environment, contact us by email of this repository.
## Contributing
We are welcome all of your pull requests! Please check out the followings:
* Write tests with RSpec
* Write code docs and README if necessary
* Send your pull request to *development* branch (Do NOT send to *master* branch)
## License
*activity_notification* project rocks and uses [MIT License](MIT-LICENSE).