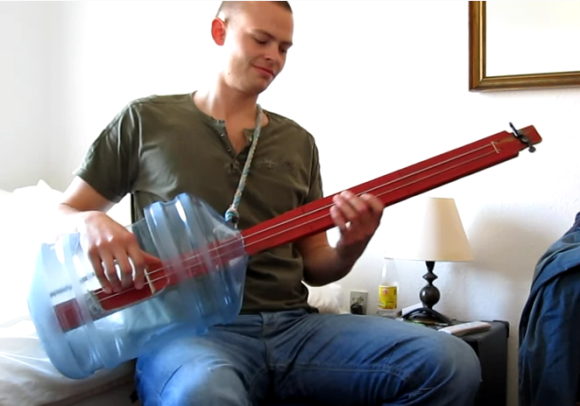

It’s easy to dismiss this one at first glance. But once you hear [Tychsen81] playing the thing you’ll want to know more.
He posted the demonstration way back in 2009. It wasn’t until a year later that he filmed the particulars of how the thing was made. The strings are actually bass guitar strings, an A and D string that are tuned down to E and A to play along with Black Sabbath’s “Ironman”. The neck is made out of two boards. One serves as the fingerboard, which is fretless. The other is mounted under that in order to provide negative space for the bridge while keeping the strings at the right height for the fingerboard. The water bottle helps to amplify the sound and that’s why the bottom end of the strings pivot on the bridge, pass through the neck, and are anchored on the bottom edge of the bottle.
We’ve embedded both the demo and the build videos after the break.
If this gets you thinking about making your own instruments you will also be interested in the Whamola.










Recent comments